Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of existing Ethernet technology that allows computer systems to communicate at speeds up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps), which is theoretically ten times the rate of existing Fast Ethernet (100-Base-T) technology.
Gigabit Ethernet is targeted at backbone networks and interserver connectivity. It provides an upgrade path for high-end workstations that require more bandwidth than Fast Ethernet can provide. This board is supported in the following systems:
Silicon Graphics Octane
Silicon Graphics Octane2
SGI Origin 200
SGI Origin 2000 (XIO adapter required)
Silicon Graphics Onyx2 (XIO adapter required)
SGI Origin 300
Silicon Graphics Onyx 300
SGI Origin 3000
Silicon Graphics Onyx 3000
Silicon Graphics Fuel
This chapter includes the following sections:
The Gigabit Ethernet board is available in two formats: the Fiber-Optic Gigabit Ethernet board and the Copper Gigabit Ethernet board. These boards are described in the following sections:
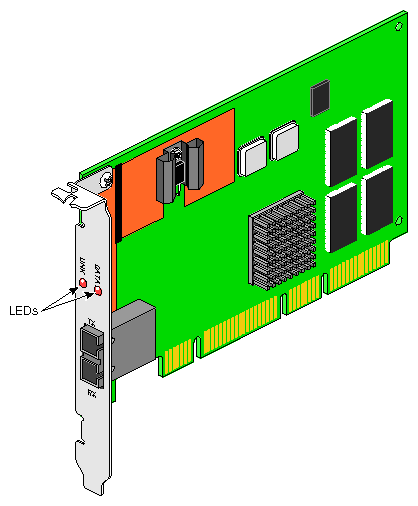
The Fiber-Optic Gigabit Ethernet board includes these features:
Full-duplex Gigabit Ethernet interface as defined in the IEEE P802.3u approved standard
Support for Ethernet frame sizes up to 9000 bytes
Dual DMA channels
ASIC with on-chip MAC and RISC processors (two)
Duplex SC fiber connector
32-/64-bit, 33-/66-MHz PCI bus interface with adaptive DMA
Universal dual-voltage signaling (3.3 V and 5 V)
Compliance with PCI Local Bus revision 2.1
For full technical specifications of the board, see Appendix A, “Specifications”.
Figure 1-1 shows the Fiber-Optic Gigabit Ethernet board.
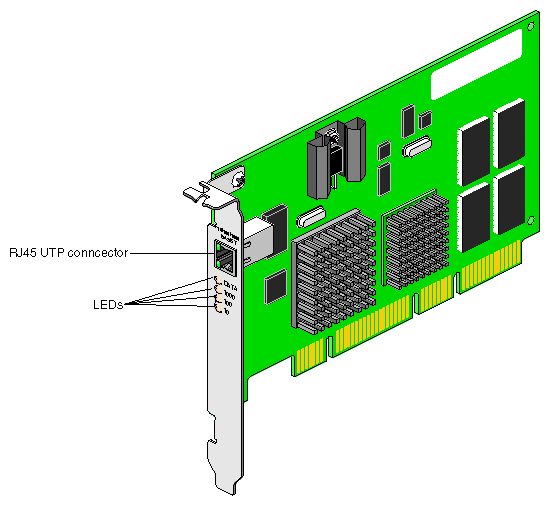
The Copper Gigabit Ethernet board includes these features:
Full-duplex Gigabit Ethernet interface as defined in the IEEE P802.3ab approved standard
Support for Ethernet frame sizes up to 9000 bytes
Dual DMA channels
ASIC with on-chip MAC and RISC processors (two)
32-/64-bit, 33-/66-MHz PCI bus interface
3Universal dual-voltage signaling (3.3 V and 5 V)
Compliance with PCI Local Bus revision 2.1
For full technical specifications of the board, see Appendix A, “Specifications”.
Figure 1-2 shows the Copper G igabit Ethe rnet board.
The cabling for the Gigabit Ethernet board is described in the following sections:
The Fiber-Optic Gigabit Ethernet board is connected to the network using fiber-optic cable. The cable, which is not included in the shipment, must be a 50-micron or 62.5-micron multimode duplex cable with an SC connector at each end. Table 1-1 lists SGI fiber-optic cables.
Table 1-1. SGI 62.5-Micron Cable Options for Fiber-Optic Gigabit Ethernet
Length | Marketing Code |
|---|---|
3 m (9.8 ft) | X-F-OPT-3M |
10 m (39.3 ft) | X-F-OPT-10M |
25 m (82 ft) | X-F-OPT-25M |
100 m (328 ft) | X-F-OPT-100M |
Table 1-2 lists operating ranges for 50-micron and 62.5-micron cables for a 1000-BASE-SX port. Fiber type is MM.
Table 1-2. Fiber-Optic Operating Range, 1000-BASE-SX Standard
Diameter (Microns) | Modal Bandwidth (MHz * km) | Range (Meters) |
|---|---|---|
62.5 | 160 | 2 to 220[a] |
62.5 | 200 | 2 to 275[b] |
50 | 400 | 2 to 500 |
5 | 500 | 2 to 550[c] |
[a] The TIA 568 building wiring standard specifies 160/500 MHz * km multimode fiber. [b] The international ISO/IEC 11801 building wiring standard specifies 200/500 MHz * km multimode fiber. [c] The ANSI Fibre Channel specification specifies 500/500 MHz * km 50 micron multimode fiber, and 500/500 MHz * km fiber has been proposed for addition to ISO/IEC 11801. | ||
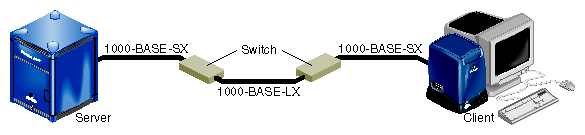
To achieve the longer distances available with 1000-Base-LX, use a switch with 1000-Base-LX ports. Figure 1-3 diagrams an example configuration.
The Copper Gigabit Ethernet board is implemented using twisted pair cable. The cable, which is not included in the shipment, must be Category-5 cable plant (4-pair) with an RJ45 UTP connector at each end. Table 1-3 lists the SGI twisted pair cables. The operating range for 1000-Base-T is up to 100 m (328 ft).
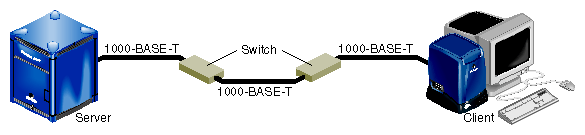
To achieve the longer distances available with 1000-Base-T, use a switch with 1000-Base-T ports. Figure 1-4 diagrams an example configuration.
Table 1-4 summarizes the configuration limits for the Fiber-Optic and Copper Gigabit Ethernet boards.
Table 1-4. Configuration Limits
System | Maximum Number of Boards |
|---|---|
Octane and Octane2 | 1 |
Origin 200 (two-CPU system) | 1 |
Origin 200 (four-CPU system) | 1 per module/2 total |
Origin 200 GIGAchannel | 1 per module/2 total |
Onyx2 deskside | 3 |
Origin 2000 and Onyx2 rackmount | 6 per module/ 6 total |
Origin 300 and Onyx 300 | 2 per system |
Origin 3000 and Onyx 3000 | 20 per system (single image) |