This chapter contains these sections:
Sound Editor allows you to create and edit audio files. For example, you can:
Record a new sound file.
Edit a sound file and cut, copy, and paste selected regions.
Add special effects to an existing sound file.
Record voice-overs for a music track.
| Note: For a more recently-developed, and more powerful, sound-editing tool, try Sound Track . |
You can open Sound Editor in one of several ways:
Click the words Sound Editor to open Sound Editor now.
To open it by clicking on an icon:
From the desktop Toolchest, select Find > Media Tools.
Double-click the Sound Editor icon.
From the command line type: soundeditor
Sound Editor provides the standard commands for opening and saving files. This section provides step-by-step instructions for using them. It contains:
To open an existing audio file, use the “Open” command on the File menu.
Choose “Open” from the File menu.
A file browser appears. If you have installed the PROSONUS™ sound library, you can find some sample sounds in the directory /usr/lib/sounds/prosonus.
Select the name of the file you want to open, then click the Open button.
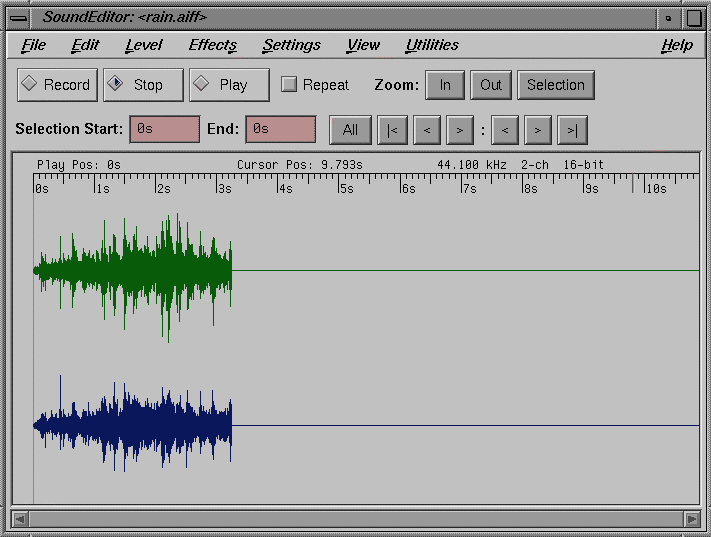
The audio waveform for that file appears in the Sound Editor display. See Figure 13-1.
Saving a file is simple. Choose “Save” or “Save As...” from the File menu. If you want to save only a selected region, choose “Save Selection.”
| Note: Sound Editor saves all files as uncompressed AIFF files. If you've inserted files of different formats, you will convert the entire track to AIFF when you save the file. Also, if you've inserted files with different sample widths, you will convert them all to the widest sample width when you save the file. |
Once you have opened a sound file or recorded a new one, you can play all of the file or just a portion of it.
To play the entire file:
place the cursor at the beginning of the waveform, then press the Play button, or
click the Select All button, the press the Play button
To play a portion of the file, place the cursor at the location at which you want to begin playing, then press the left mouse button and drag. Release the mouse button when the region you want to play is highlighted gray. Press the Play button.
| Tip: Instead of clicking the Play button, you can press the right mouse button to begin playing. |
Use the commands on the Level menu to adjust the sound level:
“Normalize” increases the level to its full dynamic range.
“Softer” decreases the level.
“Louder” increases the level.
“Set Level...” opens a dialog box in which you specify a scaling value. See “The “Set Level...” Command” for details.
This section describes three ways of recording:
You can use Sound Editor to record a new audio file. If Sound Editor isn't already running, click the words Sound Editor to open it now.
Choose “New” from the File menu.
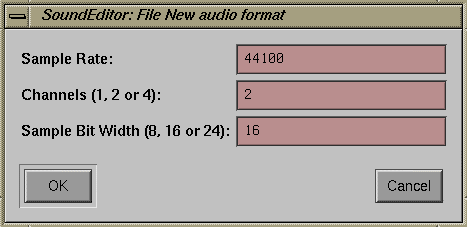
The dialog box shown in Figure 13-2 appears. You use this dialog box to specify the sample rate, sample width, and number of channels in the file.
In the dialog box, enter the sample rate, number of channels, and sample width you want to use for this recording.
The lists below show the legal values for each setting.
Sample Rate 8000
11025
16000
22050
32000
44100
48000Channels 1
2
4Sample Width 8
16
24Use the Audio Control Panel to select where you want to record from—the tape deck connected to your Line In port, for example.
To open the Audio Panel, choose “Audio Control Panel” from the Utilities menu or click the words Audio Panel now.
Choose “Microphone” from the Input menu if you want to record from the microphone.
Choose “Line” from the Input menu if you want to record from a device, such as a tape deck, connected to the Line In port on your system.
Choose “Digital”if you want to record audio from a device connected to the Digital In port on your system (if your system has Digital In).
Use the Audio Panel to adjust the input level.
The pair of sliders on the left side of the window controls the input level. For the best results, set the level to six or seven.
Press the Record button in the Sound Editor window.
Begin playing the sound you want to record. For example:
If you are recording your voice, begin speaking into the microphone.
If you are recording from a compact disc or DAT player, press the Play button on in CD Manager or DAT Manager.
If you are recording from a device, such as a tape deck, connected to the Line In port, press the Play button on the device.
Press the Stop button to signal that you are finished recording.
Choose “Save As...” from the File menu to name the file you've just created.
You can use Sound Editor to add audio to an existing file. If Sound Editor isn't already running, click the words Sound Editor to open it now.
Place the edit line in the location at which you want to insert the recording.
For example, to add a new recording at the beginning of the file, place the edit line at the beginning of the waveform. See “Placing the Edit Line” for details.
Use the Audio Panel to select where you want to record from—the microphone or a compact disc player, for example.
To open the Audio Panel, choose “Audio Control Panel” from the Utilities menu or click the words Audio Panel now.
Choose “Microphone” from the Input menu if you want to record from the microphone.
Choose “Line” from the Input menu if you want to record from a device, such as a tape deck or VCR, connected to the Line In port on your system.
Choose “Digital” if you want to record audio from a device connected to the Digital In port on your system (if your system has Digital In).
Use the Audio Panel to adjust the input level.
The pair of sliders on the left side of the window controls the input volume. For the best results, set the input level to six or seven.
Press the Record button in the Sound Editor window.
Begin playing the sound you want to record. For example:
If you are recording your voice, begin speaking into the microphone.
If you are recording from a compact disc or DAT player, press the Play button in CD Manager or DAT Manager.
If you are recording from a device, such as a tape deck, connected to the Line In port, press the Play button on the device.
Press the Stop button to signal that you are finished recording.
Suppose you have a music track and you'd like to overlay it with a recording of someone talking. You can use the “Overdub Record” command to do so.
Open the audio file over which you want to record your voice.
Choose “Overdub Record” from the Settings menu.
The Record button changes its name; now it's labeled Overdub.
Place the edit line in the waveform where you want the voice overlay to begin.
See “Placing the Edit Line” for details on using the edit line.
Select an input source and adjust the input level according to the instructions in “Recording a New Sound File.”
Click Overdub to begin recording.
Click Stop to signal you are finished recording.
Once you have opened or recorded a sound file, you can modify it in several ways. This section provides instructions for:
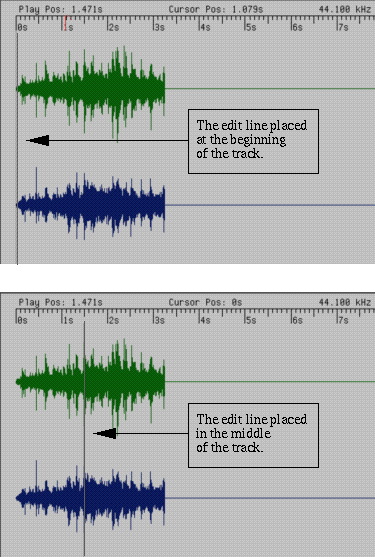
To edit a sound file, you first need to learn how to recognize and place the edit line in the waveform display. Figure 13-3 shows the edit line in two locations—the beginning of the track and midway through the track. The edit line appears as a faint gray line.
To position the edit line, place the cursor over the waveform, then click the left mouse button. The edit line appears at the cursor location. To reposition the edit line, place the cursor in a different location, then click the left mouse button again.
You need to select a region of sound if you want to play that portion of the sound track, cut, copy, or paste that portion, or perform some special effects on it. This section provides instructions for:
To select the entire track, click the Select All button or choose “Select All” from the Edit menu. The entire waveform is highlighted gray.
To select a portion of the track, place the cursor over the waveform, then press the left mouse button and drag the cursor. Detailed instructions follow:
Move the cursor into the waveform, then click and hold down the left mouse button.
The edit line appears at the cursor location.
Continue pressing the left mouse button and drag the cursor to highlight a portion of the waveform.
The selected region is highlighted gray.
Release the mouse button when the area you want is highlighted.
The beginning and end of a selection appears in the Selection Start and End fields above the waveform. You can also select a section of the track by typing numbers into these fields. For example, if you wanted to select the section of the track beginning with 1.1s and ending with 2.8s, you would type 1.1 into the Start field and 2.8 into the End field. Hit <Enter> after each entry. The section is selected.
| Tip: You can use the <<, <, >, and >> buttons to make fine adjustments to the selection. See “The Selection Controls” for details. |
To remove a section of audio from the sound track, you can use the “Cut” or “Delete” commands. Use the “Cut” command if you want to cut the selection and place it elsewhere in the track; use the “Delete” command to remove the section permanently.
Select the region of audio you want to remove.
The selected region is highlighted gray. See “Selecting a Portion of the Track” for detailed instructions.
Choose “Cut” or “Delete” from the Edit menu.
Choose “Cut” if you want to cut the region and use the “Paste” command to place the selection elsewhere in the file.
Choose “Delete” or press the <BackSpace> key if you want to remove that region.
| Note: “Cut” and “Delete” let you remove the selected region. The “Trim” command does just the opposite. Choose “Trim” to delete everything except the selected region. |
In a text editor, if you select a word and begin typing, you replace the selected word with the word you type. The same is true with audio. Select a region of sound and you can easily replace it.
Select the region of audio you want to replace.
The selected region is highlighted gray. See “Selecting a Portion of the Track” for detailed instructions.
Replace the selected by audio by doing one of the following:
Replace the audio with silence by choosing “Clear” from the Edit menu.
Replace the selected region with another audio file by choosing “Insert...” from the File menu.
Replace the audio with a new recording by following the instructions in “Recording into an Existing Sound File.”
To copy a region of sound, select the region, then use the “Copy” and “Paste” commands on the Edit menu.
Select the region of audio you want to copy.
The selected region is highlighted gray. See “Selecting a Portion of the Track” for detailed instructions.
See “Selecting a Portion of the Track” for detailed instructions.
Choose “Copy” from the Edit menu.
Position the edit line where you want the sound to be pasted.
If you want to substitute this for some existing sound, use the edit line to select a region to replace. See “Placing the Edit Line” for more information on the edit line.
Choose “Paste” from the Edit menu.
The copy is inserted immediately after the edit line or over the selected region of audio.
| Tip: Instead of using the “Copy” and “Paste” commands, you can select a region of sound, then click the middle mouse button to paste a copy elsewhere in the track. The audio appears at the cursor location, not the edit line location. |
The “Mix” commands lets you combine two portions of sound. To use it:
Select the section of sound you want to mix with another section, then choose “Cut” or “Copy” from the Edit menu.
The selection is copied onto a temporary clipboard.
Select another section of audio elsewhere in the file.
The selected region is highlighted gray.
Choose “Mix” from the Edit menu.
The audio you cut or copied is mixed with the selected portion. To undo this action, choose “Undo mix” from the Edit menu.
The Effects menu contains commands for applying simple special effects. You can fade audio in and out, play it in reverse, add echoes, or adjust the playback speed. See “The Effects Menu” for details on each of the commands.
This section provides a list of problems you might encounter and offers possible solutions.
You hear no sound when playing all or part of a file.
Make sure the edit line in the waveform is not at the end of the file. This line marks the beginning of play. Also, open the Audio Panel and verify that the left and right Headphone/Speaker Output levels, which control the volume, are up.
To open the Audio Panel, choose “Audio Control Panel” from the Utilities menu or click the words Audio Panel now.
The recording is too soft, even with the volume turned all the way up.
Try choosing “Louder” from the Levels menu or choose “Normalize” to automatically raise the level of recording to fill the full dynamic range.
The recording is too loud, even with the volume turned all the way down.
Try choosing “Soften” from the Levels menu until the volume reaches a desired level.
Material that was deleted cannot be pasted.
Remember that “Delete” cuts the selection but does not save it to the Clipboard. Always use “Cut” when you want to cut and paste.
The audio sounds like it's playing through a loudspeaker.
Open the Audio Panel. If the Monitor button is on, you will hear the input signal along with the recording. Click this button off if you do not want to hear it. The red checkmark disappears when it's disabled.
To open the Audio Panel, choose “Audio Control Panel” from the Utilities menu or click the words Audio Panel now.
Sound isn't recording through the microphone.
Start by making sure the microphone cable is connected correctly. After that, open the Audio Panel to make sure “Microphone” is selected as the input source. Also make sure the left and right Input Levels, which adjust the volume, are up.
To open the Audio Panel, choose “Audio Control Panel” from the Utilities menu or click the words Audio Panel now.
This section describes the controls you see in the Sound Editor display. It contains information about:
The top portion of the Sound Editor window contains the buttons you use to record and play sound files.
| Record | Click Record when you are ready to begin recording. The new audio appears at the location of the edit line. | |
| Stop | Click Stop when you are finished recording or want to stop playing the sound file. | |
| Play | Click Play to play the sound file or a selected region of the file. | |
| Repeat | Click Repeat if you want to play the sound file repeatedly. |
The In, Out, and Selection buttons let you alter the waveform display. Click In to display the waveform in smaller time increments; click Out to display the waveform in larger time increments; click Selection to fill the display with the selected region.
The selection controls shown in Table 13-1 let you fine-tune your selection or the placement of the edit line.
Table 13-1. Purpose of the selection controls
Button | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Selects the entire sound track. | ||
Extends the selection to the beginning of the sound track.
| ||
Give you finer control for adjusting the start or end points of the selected region. | ||
Extends the selection to the end of the sound track. |
The waveform display and timeline represent the open audio file. Above the timeline, you see four fields:
| Time | Indicates where you are in the file as it is playing. | |
| Selection | Indicates the span of a selected region. This will be a single number (the location of the edit line) if you have not selected a region. | |
| Rate | Indicates the sample rate at which the file was recorded. Higher sample rates yield better audio fidelity but also take up more disk space. | |
| Position | Indicates the location of the cursor in the timeline. |
This section provides information on each of the menus and commands used in Sound Editor. It contains:
The “Utilities Menu”
Also see “Using Sound Editor's Menus.”
The commands on the file menu let you create new files, open and save existing files, and insert one file into another. The commands are:
Choose “New...” when you want to create a new audio file. A dialog box appears asking you to specify the sample rate, number of channels, and sample width for the new file. See “Recording a New Sound File” for detailed instructions.
Choose “Insert...” if you want to insert one audio file into another. For example, suppose you have a bit of music that you want to place at the beginning of a sound track. Place the edit line at the beginning of the waveform, then choose “Insert...” You can also use this command to replace the selected region of audio.
Choose “Save” to save the changes that you've made to a file.
Sound Editor saves all files as uncompressed AIFF files. If you've inserted files of different formats, you will convert the entire track to AIFF when you save the file. Also, if you've inserted files with different sample widths, you will convert them all to the widest sample width when you save the file.
Choose “Save Selection...” when you want to save the selected region to a file. You'll find this useful if you need to create many “sound bites” from one audio file.
The commands on the Edit menu let you cut, copy, and paste selected sections of audio. The commands are:
Choose “Undo” to reverse your last action. For example, if you've used the “Cut” command to remove a section of audio, you can choose “Undo cut” to restore the section.
Choose “Cut” when you want to delete a section of audio or move it to a different location in the soundtrack. The selected section disappears from the waveform and is placed in a temporary clipboard. Use the “Paste” command to place the selection elsewhere in the file. See “Deleting a Section of Audio” for step-by-step instructions.
Choose “Copy” when you want to duplicate a section of audio. The copy is placed on a temporary clipboard. Choose “Paste” when you're ready to paste the copy elsewhere in the file. See “Copying and Pasting Audio” for details.
Choose the “Paste” command after you've used the “Cut” or “Copy” command. It retrieves the selection from the temporary clipboard and inserts it at the edit line.
Choose “Mix” after you've used the “Cut” or “Copy” command. It lets you mix the sound you've cut or copied with the section of sound you have selected.
Choose “Clear” to replace a selected section of audio with silence. That area of the waveform appears blank.
Choose “Delete” to remove a selected section from the soundtrack. This is equivalent to pressing the <Back Space> key on the keyboard.
| Note: You cannot use the “Paste” command to paste audio sections that have been removed using the “Delete” command. If you want to remove a section and place it elsewhere in the file, use the “Cut” command. |
Whenever you select a region of audio or use the “Cut” and “Copy” commands, you store a temporary copy of that information on an invisible clipboard. When you use the “Paste” command or press the middle mouse button, you paste a copy of whatever information is stored on the clipboard. This does not delete information from the clipboard.
Clipboard data take up disk space and system memory. If you are low on disk space and have copied a large region of audio, consider choosing “Empty Clipboard” from the Edit menu.
The commands on the Level menu let you adjust the loudness of the sound sample. They are:
Choose “Normalize” to increase the sound level of the selected section to its full dynamic range. To increase the level for the entire file, click Select All before choosing “Normalize.”
Choose “Softer” to decrease the volume of a selected section. To lower the volume of the entire file, click Select All before choosing “Softer.”
Choose “Louder” to increase the volume of a selected section. To raise the volume of the entire file, click Select All before choosing “Louder.”
Choose the “Set Level...” command to manually adjust the volume of the selected section. A dialog box appears into which you type the new scaling value. For example, if you want to value to be 50 percent lower, type .50 in the dialog box. The height of the waveform is reduced by half.
The commands on the Effects menu let you alter selected sound in a variety of ways. The choices are:
Choose “Fade In” to cause sound at the beginning of the selected section to start out from silence and gradually increase to its normal volume.
Choose “Fade Out” to cause sound at the end of a selected section to gradually decrease in volume to silence.
The commands on the View menu let you change your view of the waveform—zoom in, zoom out, or zoom in on a particular section.
The commands are:
Choose “Zoom In” to display the waveform in smaller time increments. This makes it easier to edit audio when you need finer resolution. “Zoom In” is equivalent to the In button.
Choose “Zoom Out” to display the waveform in larger time increments. Zooming out is useful when you want to edit large regions of audio. “Zoom Out” is equivalent to the Out button.
The Settings menu contains the “Overdub Record” command:
The “Overdub Record” command lets you record audio and mix it with audio you've previously recorded. See “Using the “Overdub Record” Command to Record Voice Overs” for details.