This chapter describes how to create ToolTalk specs for objects your application creates and manages. Before you can identify the type of objects, you need to define otypes and store them in the types database. See Chapter 4, “Static Message Patterns,” for information on otypes.
The ToolTalk service uses spec and otype information to determine object–oriented message recipients.
Object-oriented messages are addressed to objects managed by applications. To use object-oriented messaging, you need to be familiar with process–oriented messaging concepts and the ToolTalk concept of object.
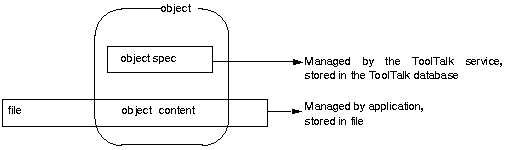
Object data is stored in two parts as shown in Figure 7-1.
One part is called the object content. The object content is managed by the application that creates or manages the object and is typically a piece, or pieces, of an ordinary file: a paragraph, a source code function, or a range of spreadsheet cells, for example.
The second part is called the object specification (spec). A spec contains standard properties such as the type of object, the name of the file in which the object contents are located, and the object owner. Applications can also add their own properties to a spec, for example, the location of the object content within a file. Because applications can store additional information in specs, you can identify data in existing files as objects without changing the formats of the files. You can also create objects of pieces of read-only files. Applications create and write specs to the ToolTalk database managed by rpc.ttdbserverd.
| Note: You cannot create objects in files that reside in a read-only file system. The ToolTalk service must be able to create a database in the same file system that contains the object. |
A ToolTalk object is a portion of application data for which a ToolTalk spec has been created.
To instruct the ToolTalk service to deliver messages to your objects, you create a spec that identifies the object and its otype. Table 7-1 lists the ToolTalk functions you use to create and write object spec.
Table 7-1. Functions to Create
Return Type | ToolTalk Function |
|---|---|
char * | tt_spec_create(const char *filepath) |
Tt_status | tt_spec_prop_set(const char *objid, |
Tt_status | tt_spec_prop_add(const char *objid, |
Tt_status | tt_spec_bprop_add(const char *objid, |
Tt_status | tt_spec_bprop_set(const char *objid, |
Tt_status | tt_spec_type_set(const char *objid, |
Tt_status | tt_spec_write(const char *objid) |
To create an object spec in memory and obtain an objid for the object, use tt_spec_create().
To assign an otype for the object spec, use tt_spec_type_set(). You must set the type before the spec is written for the first time. It cannot be changed.
| Note: If you create an object spec without assigning an otype or with an otype that is unknown to the types database, messages addressed to the object cannot be delivered. (The ToolTalk service does not verify that the otype you specified is known to the types database.) |
You can determine what properties you want associated with an object; you add these properties to a spec. The ToolTalk service recognizes that it is not always possible to store information in your own internal data; for example, the objid for objects in plain ASCII text files. You can store the location of the objid in a spec property and then use this location to identify where the object is in your tool's internal data structures.
The spec properties are also a convenience for the user. A user may want to associate properties (such as a comment or object name) with the object that they can view later. Your application or another ToolTalk-based tool can search for and display these properties for the user.
After you set the otype and add properties to an object spec, use tt_spec_write() to make it a permanent ToolTalk item and visible to other applications. When you call tt_spec_write(), the ToolTalk service writes the spec into the ToolTalk database.
To update existing object spec properties, use tt_spec_prop_set() and tt_spec_prop_add() specifying the objid of the existing spec. Once the spec properties are updated, use tt_spec_write() to write the changes into the ToolTalk database.
When you are updating an existing spec and the ToolTalk service returns TT_WRN_STALE_OBJID when you call tt_spec_write(), it has found a forwarding pointer to the object in the ToolTalk database that indicates the object has been moved. To obtain the new objid, create an object message that contains the old objid and send it. The ToolTalk service will return the same status code, TT_WRN_STALE_OBJID, but updates the message objid attribute to contain the new objid. Use tt_message_object() to retrieve the new objid from the message and put the new objid into your internal data structure.
The ToolTalk service provides the functions to examine, compare, query, and move object specs. Table 7-2 lists the ToolTalk functions you use to maintain object specs.
Table 7-2. Functions to Maintain Object Specifications
Return Type | ToolTalk Function |
|---|---|
char * | tt_spec_file(const char *objid) |
char * | tt_spec_type(const char *objid) |
char * | tt_spec_prop(const char *objid, |
int | tt_spec_prop_count(const char *objid, |
Tt_status | tt_spec_bprop(const char *objid, |
char * | tt_spec_propname(const char *objid, int n) |
int | tt_spec_propnames_count(const char *objid) |
char * | tt_objid_objkey(const char *objid) |
Tt_status | tt_file_objects_query(const char *filepath, Tt_filter_function filter, void *context, void *accumulator) |
int | tt_objid_equal(const char *objid1, |
char * | tt_spec_move(const char *objid, |
To compare two objids, use tt_objid_equal(). tt_objid_equal()returns a value of 1 even in the case where one objid is a forwarding pointer for the other.
Create a filter function to query for specific specs in a file and obtain the specs in which you are interested.
Use tt_file_objects_query() to find all the objects in the named file. As the ToolTalk service finds each object, it calls your filter function, and passes it the objid of the object and the two application-supplied pointers. Your filter function does some computation and returns a Tt_filter_action value (TT_FILTER_CONTINUE or TT_FILTER_STOP) to either continue the query, or to quit the search and return immediately.
The following sample code illustrates how to obtain a list of specs:
/*
* Called to update the scrolling list of objects for a file.
* Uses tt_file_objects_query to find all the ToolTalk objects.
*/
int
cntl_update_obj_panel()
{
static int list_item = 0;
char *file;
int i;
cntl_objid = (char *)0;
for (i = list_item; i >= 0; i--) {
xv_set(cntl_ui_olist, PANEL_LIST_DELETE, i, NULL);
}
list_item = 0;
file = (char *)xv_get(cntl_ui_file_field, PANEL_VALUE);
if (tt_file_objects_query(file,
if (tt_file_objects_query(file,
(Tt_filter_function)cntl_gather_specs,
&list_item, NULL) != TT_OK)
{
xv_set(cntl_ui_base_window, FRAME_LEFT_FOOTER,
“Couldn't query objects for file”, NULL);
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
|
Within the tt_file_objects_query() function, the application calls cntl_gather_specs, a filter function that inserts objects into a scrolling list.
/*
* Function to insert the objid given into the scrolling lists
* of objects for a file. Used inside tt_file_objects_query as
* it iterates through all the ToolTalk objects in a file.
*/
Tt_filter_action
cntl_gather_specs(objid, list_count, acc)
char *objid;
void *list_count;
void *acc;
{
int *i = (int *)list_count;
xv_set(cntl_ui_olist, PANEL_LIST_INSERT, *i,
PANEL_LIST_STRING, *i, objid,
NULL);
*i = (*i + 1);
/* continue processing */
return TT_FILTER_CONTINUE;
}
|
The objid contains a pointer to a particular file system where the spec information is stored. To keep spec information as available as the object described by the spec, the ToolTalk service stores the spec information on the same file system as the object. Therefore, if the object moves, the spec must move, too.
Use tt_spec_move() to notify the ToolTalk service when an object moves from one file to another (for example, through a cut and paste operation).
If a new objid is not required (because both the new and old files are in the same file system), the ToolTalk service returns TT_WRN_SAME_OBJID.
If the object moved to another file system, the ToolTalk service returns a new objid for the object and leaves a forwarding pointer in the ToolTalk database from the old objid to the new one.
When your process sends a message to an out-of-date objid (that is, one with a forwarding pointer), tt_message_send() returns a special status code, TT_WRN_STALE_OBJID, and replaces the object attribute in the message with a new objid that points to the same object in the new location.
| Note: Update any internal data structures that reference the object with the new objid. |
To keep the ToolTalk database that services the disk partition where a file that contains object data is stored up-to-date, use the ToolTalk functions to copy, move, or destroy the file. Table 7-3 lists the ToolTalk functions you use to manage files that contain object data.
Table 7-3. Functions to Copy, Move, or Remove Files that Contain Object Data
Return Type | ToolTalk Functions |
|---|---|
Tt_status | tt_file_move(const char *oldfilepath, const char *newfilepath) |
Tt_status | tt_file_copy(const char *oldfilepath, const char *newfilepath) |
Tt_status | tt_file_destroy(const char *filepath) |
The ToolTalk service provides ToolTalk-enhanced shell commands to copy, move, and remove ToolTalk object and file information. Table 7-4 lists the ToolTalk-enhanced shell commands that you and users of your application should use to copy, move, and remove files referenced in messages and files that contain objects.
Table 7-4. ToolTalk-Wrapped Shell Commands
Command | Description |
|---|---|
ttcopy | Copies file to new location. Updates file and object location information in ToolTalk database. |
ttmv | Moves directory or files to new location. Updates file and object location information in ToolTalk database. Removes old version of file or directory. |
ttrm | Removes specified file. Removes file and object information from the ToolTalk database. |
ttrmdir | Removes empty directories (directories that contain no files) that have ToolTalk object specs associated with them. It is possible to create an object spec for a directory; when an object spec is created, the path name of a file or directory is supplied. Removes object information from the ToolTalk database. |
tttar | Archives or extracts multiple files and object information into (or from) a single archive, called a tarfile. Can also be used to only archive or extract ToolTalk file and object information into (or from) a tarfile. |
The following sample code creates an object for its user: it creates the object spec, sets the otype, writes the spec to the ToolTalk database, and wraps the user's selection with C-style comments. The application also sends out a procedure-addressed notice after it creates the new object to update other applications who observe messages with the Sun_EditDemo_new_object operation. If other applications are displaying a list of objects in a file managed by Sun_EditDemo, they update their list after receiving this notice.
/*
* Make a ToolTalk spec out of the selected text in this
* textpane. Once the spec is successfully created and written
* to a database, wrap the text with C-style comments in order
* to delimit the object and send out a notification that an
* object has been created in this file.
*/
Menu_item
edit_ui_make_object(item, event)
Panel_itemitem;
Event*event;
{
int mark = tt_mark();
char*objid;
char*file;
char*sel;
Textsw_indexfirst, last;
charobj_start_text[100];
charobj_end_text[100];
Tt_message msg;
if (! get_selection(edit_ui_xserver, edit_ui_textpane,
&sel, &first, &last)) {
xv_set(edit_ui_base_window, FRAME_LEFT_FOOTER,
“First select some text”, NULL);
tt_release(mark);
return item;
}
file = tt_default_file();
if (file == (char *)0) {
xv_set(edit_ui_base_window, FRAME_LEFT_FOOTER,
“Not editing any file”, NULL);
tt_release(mark);
return item;
}
/* create a new spec */
objid = tt_spec_create(tt_default_file());
if (tt_pointer_error(objid) != TT_OK) {
xv_set(edit_ui_base_window, FRAME_LEFT_FOOTER,
“Couldn't create object”, NULL);
tt_release(mark);
return item;
}
/* set its otype */
tt_spec_type_set(objid, “Sun_EditDemo_object”);
if (tt_spec_write(objid) != TT_OK) {
xv_set(edit_ui_base_window, FRAME_LEFT_FOOTER,
“Couldn't write out object”, NULL);
tt_release(mark);
return item;
}
/* wrap spec's contents (the selected text) with C-style */
/* comments. */
sprintf(obj_start_text,” /* begin_object(%s) */”, objid);
sprintf(obj_end_text,” /* end_object(%s) */”, objid);
(void)wrap_selection(edit_ui_xserver, edit_ui_textpane,
obj_start_text, obj_end_text);
/* now send out a notification that we've added a new object */
msg = tt_pnotice_create (TT_FILE_IN_SESSION,
”Sun_EditDemo_new_object”);
tt_message_file_set(msg, file);
tt_message_send(msg);
tt_release(mark);
return item;
}
|