The EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture) bus is supported by the Silicon Graphics Indigo2, POWER Indigo2, and Indigo2 Maximum Impact systems. This chapter contains the following topics related to support for the EISA bus:
“The EISA Bus in SGI Systems” gives an overview of the EISA bus features and implementation.
“Kernel Functions for EISA Support” discusses the kernel functions that are specifically used by EISA device drivers.
“Sample EISA Driver Code” displays a complete character driver for an EISA device.

Note: Often it is most practical to control an EISA device through programmed I/O from a user-level process. For information on PIO, turn to “EISA Programmed I/O” in Chapter 4 after reading “The EISA Bus in SGI Systems”. For information on the general architecture of a kernel-level device driver, see Part III, “Kernel-Level Drivers”.
The EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture) bus is an enhancement of the ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) bus standard originally developed by IBM.
EISA is backward compatible with ISA, but expands the ISA data bus from 16 bits to 32 bits, and provides 23 more address lines and 16 more indicator and control lines. The EISA bus supports the following features:
all ISA transfers
bus master devices
burst-mode DMA transfers
32-bit data and address paths
peer-to-peer card communication
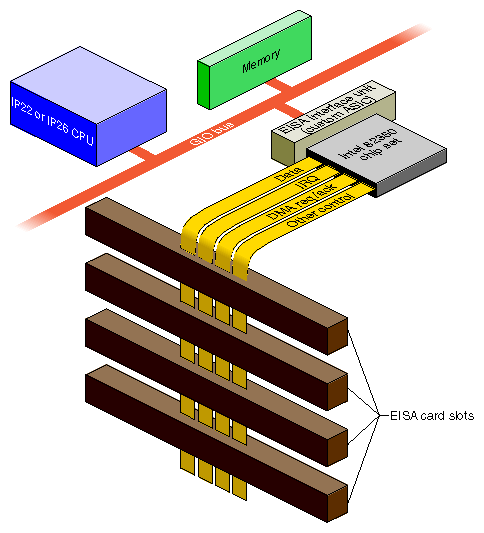
For detailed information on EISA-bus protocols, electrical specifications, and operation, see the standards documents (“Standards Documents”). Figure 18-1 shows the high-level design of the EISA attachment in the Indigo2 architecture.
EISA provides server DMA channels arranged into two channel groups (channels 0-3 and channels 5-7) for priority resolution. SGI uses the rotating scheme described in the EISA specification. Although the channels rotate in this scheme, channels 5-7 receive more cycles, in general, than channels 0-3.
The EISA bus supports 11 edge-triggerable or level-triggerable interrupts. IRQ0–IRQ2, IRQ8, and IRQ13 are reserved for internal functions and are not available to EISA cards. The remaining 11 interrupt lines (IRQ3–IRQ7, IRQ9–IRQ12, IRQ14, IRQ15) can be generated by EISA cards. Multiple cards can use one IRQ level, so long as they use the same triggering method.
All EISA-generated interrupts are transmitted to a single interrupt level on the Silicon Graphics CPU (see “Interrupt Priority Scheduling”).
The EISA bus supports 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit data transfers through direct CPU access (PIO) as well as DMA initiated by a bus-master card or the on-board DMA hardware.
The EISA-bus address space is divided into I/O address space and memory address space. On the EISA bus, accesses to memory and to I/O are distinguished by having different bus cycle protocols. The MIPS architecture has only one type of memory access, so in the Silicon Graphics systems, EISA I/O space and memory space are assigned separate ranges of physical addresses. The EISA Interface Unit (see Figure 18-1) decodes the address ranges and causes the Intel 82350 bus control to issue the appropriate bus cycle type, I/O or memory.
The I/O address space comprises a sequence of 4 KB page, one for each bus slot. The first page, slot 0, corresponds to the registers of the Intel 82350 chip set. The pages for slots 1-4 correspond to the four accessible slots in the Indigo2 and Challenge M chassis (see “Available Card Slots”).
The EISA bus architecture provides a signal, LOCK*, which allows a card (or the processor, in an Intel architecture system) to lock bus access so as to perform one or more atomic updates.
The Silicon Graphics hardware implementation of the EISA bus is bridged onto the GIO bus, which does not support a locked cycle. The general form of locked bus cycles is not supported in the Silicon Graphics implementation of EISA. An EISA card cannot lock the bus nor can software in the IRIX kernel lock the EISA bus.
A device driver in the IRIX kernel can perform a software-controlled read-modify-write cycle, as on a VME bus, using the pio_*_rmw() kernel functions. See (“Using the PIO Map in Functions”). This function ensures that no other software accesses the EISA bus during the read-modify-write operation.
An important implementation detail of the EISA bus is that it uses the Intel convention of “little-endian” byte ordering, in which the least significant byte of a halfword or word is in the lowest address. The Silicon Graphics CPU uses “big-endian” ordering, with the most significant byte first. Hence data exchanged with the EISA bus often needs to be reordered before use.
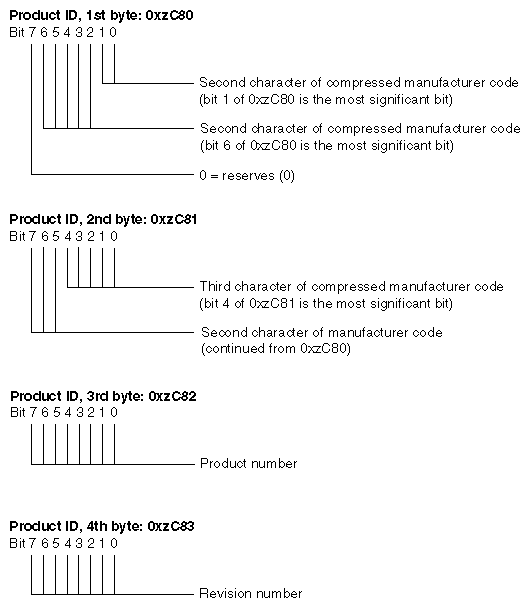
EISA expansion boards, embedded devices, and system boards have a four-byte product identifier (ID) that can be read from I/O port addresses 0xsC80 through 0xsC83 in the card's I/O address space, where s is the offset of the card slot. For example, the slot 1 product ID can be read as a 4-byte value from I/O port addresses 0x1C80. This value can be tested in an exprobe parameter of the VECTOR line during system boot (see “Configuring IRIX”).
The first two bytes (0xsC80 and 0xsC81) contain a compressed representation of the manufacturer code. The manufacturer code is a three-character code (uppercase ASCII characters in the range of A to Z) chosen by the manufacturer and registered with the standard (see “Standards Documents”). The manufacturer code “ISA” is used to indicate a generic ISA adapter.
Figure 18-2 summarizes the contents of the EISA manufacturer ID value.
The three-character manufacturer code is compressed into three 5-bit values so that it can be incorporated into the two I/O bytes at 0xsC80 and 0xsC81. The compression procedure is as follows:
Find the hexadecimal ASCII value for each letter:
ASCII for “A”-“Z”: “A” = 0x41, “Z” = 0x5a
Subtract 0x40 from each ASCII value:
Compressed “A” = 0x41-0x40 = 0x01 = 0000 0001
Compressed “Z” = 0x5a-0x40 = 0x1A = 0001 1010Discard leading 0-bits, retaining the five least significant bits of each letter:
Compressed “A” = 00001. Compressed “Z” = 11010
Compressed code = concatenate “0” and the three 5-bit values:
“AZA” = 0 00001 11010 00001
One or more EISA cards can be plugged into an Indigo2 series workstation, or into a Challenge M system (which uses the identical chassis). Any EISA-conforming card can be plugged into an available slot. EISA devices can be used as block devices or character devices, but they cannot be used as boot devices.
The Indigo2 series has four peripheral card slots that accept graphics adapters, EISA cards, or GIO cards in any combination. Graphics cards are available that use one, two, or three slots, resulting in the following combinations:
With Extreme graphics installed, one slot is available for use by an EISA card.
With XZ graphics installed, two slots are used by the graphics, and two are available for EISA cards.
The XL graphics uses only one slot, so up to three EISA cards can be accommodated.
The Challenge M system, having no graphics adapter, has four available slots.
The pages of EISA I/O address space are mapped to physical addresses 0x0001 0000 (slot 1) through 0x0004 0000 (slot 4). The 112 MB of EISA memory address space is mapped to physical addresses between 0x000A 0000 and 0x06FF FFFF. Addresses in these ranges can be mapped into the kernel address space for PIO or for DMA (see “Kernel Functions for EISA Support”).
The EISA architecture associates interrupt priority with the IRQ level, from IRQ0 to IRQ15. In Silicon Graphics systems, all EISA interrupts are channeled into one CPU interrupt level. The priority of this CPU interrupt is below that of the clock and at the same level as on-board devices. When multiple EISA interrupts arrive, they are serviced in their EISA-bus priority order. When the CPU receives an EISA-bus interrupt, it responds to each interrupt level in IRQ priority order (lower number first). For each interrupt level, the IRIX kernel calls one or more interrupt service functions that have been established by device drivers (see “Allocating IRQs and Channels”).
In order to integrate an EISA device into a Silicon Graphics system you must configure the EISA card itself, and then configure the system to recognize the card.
The I/O address space on an EISA card plugged into a card slot responds to the range of bus addresses for that slot. All EISA cards are identified by a manufacturer-specific device ID that the operating system uses to register the existence of each card. ISA cards, in contrast, are jumpered to respond to a specific address range that corresponds to the device's I/O registers.
Normally a kernel-level driver accesses registers in the I/O space using a PIO map (see “Mapping PIO Addresses”). For a card's memory space to be accessible, the card must be configured or jumpered to respond to the appropriate address range. The specified address range must be selected to avoid conflicts with other EISA/ISA devices.
In the PC/DOS hardware and software environment, where the EISA bus is commonly found, device configuration is handled in part by use of a standalone ROM BIOS initialization program that stores device information in the nonvolatile RAM of the PC; and in part by saving device initialization information in configuration files that are read at boot time.
Neither of these facilities is available in the same way under IRIX. Each EISA device is configured to IRIX using a VECTOR line in a file stored in the directory /var/sysgen/system (see “Kernel Configuration Files” in Chapter 2).
The syntax of a VECTOR line is documented in two places:
The /var/sysgen/system/irix.sm file itself contains descriptive comments on the syntax and meaning of the statement, as well as numerous examples.
The system(4) reference page gives a more formal definition of the syntax.
In a Silicon Graphics system equipped with an EISA bus, the file /var/sysgen/system/irix.sm contains a number of VECTOR lines describing the EISA devices supported by distributed code.
The important elements in a VECTOR line for EISA are as follows:
bustype | Specified as EISA for EISA devices. The VECTOR statement can be used for other types of buses as well. |
module | The base name of a kernel-level device driver for this device, as used in the /var/sysgen/master.d database (see “Master Configuration Database” in Chapter 2 and “How Names Are Used in Configuration” in Chapter 9 ). |
adapter | The number of the EISA bus where the device is attached—always 0, or omitted, in current systems. |
ctlr | The “controller” number is simply an integer parameter that is passed to the device driver at boot time. It can be used for example to specify a slot number. |
iospace, iospace2, iospace3 | Each iospace group specifies the address space, the starting address, and the size of a segment of address space used by this device. |
probe or exprobe | Specifies a hardware test that can be applied at boot time to find out if the device exists. |
The following is a typical VECTOR line for an EISA device (it must be a single physical line in the file):
VECTOR: bustype=EISA module=if_ec3 ctlr=1 iospace=(EISAIO,0x1000,0x1000) exprobe_space=(r,EISAIO, 0x1c80,4,0x6010d425,0xffffffff) |
The iospace, iospace2, and iospace3 parameters are used to pass ranges of device addresses to the device driver. Each parameter contains the following three items:
A keyword for the address space, either EISAIO or EISAMEM.
The starting address, which depends on the address space and the card itself, as follows:
For the I/O space of an EISA card, the starting address of I/O registers is 0x1000 multiplied by the slot number of the card (from 1 to 4), and extends for a length of 0x1000 (4096). For example, the manufacturer ID of the card in slot 2 is at address 0x1C80.
The I/O space of an ISA card is hard-wired or jumpered on the card, and falls in the range 0x0100 to 0x0400.
The EISAMEM space is card-dependent and falls in the range 0x000A 0000 through 0x06FF FFFF.
The length of this bus address range.
The values in these parameters are passed to the device driver at its pfxedtinit() entry point, provided that the probe shows the device is active.
You use the probe or exprobe parameter to program a test for the existence of the device at boot time. When no test is specified, lboot assumes the device exists. Then it is up to the device driver to determine if the device is active and usable. When the device does not respond to a probe (because it is off-line or because it has been removed from the system), the lboot command will not invoke the device driver for this device.
An example exprobe parameter is as follows:
exprobe_space=(r,EISAIO, 0x1c80,4,0x6010d425,0xffffffff) |
The exprobe parameter lists groups of six subparameters, as follows:
Sequence | One or more of w for write, r for read, or rn for read-negate. |
Space | EISAIO or EISAMEM. |
Address | The address of the byte, halfword, or word to test. |
Length | The number of bytes to test: 1, 2, or 4. |
Value | The value to write, or the test value for a read. |
Mask | A number to be ANDed with the Value operand before a write or after a read. Specify 0xffffffff to nullify the AND operation. |
You can use the w operation to prime a device. You can use the r operation to test for a specific value, and the rn operation to test that a specific value (or a specific bit, after masking) is not returned.
Typically, a simple r operation is used on an EISA card to test for the manufacturer's product identifier.
To test the existence of an ISA card, use a wr sequence to write a value to a register and read it back unchanged. Or read a value and verify that it does not come back all-binary-1, the value returned by a nonexistent device.
The device driver specified by the module parameter is invoked at its pfxedtinit() entry point, where it receives ctlr and iospace information specified in the VECTOR line (see “Entry Point edtinit()” in Chapter 7). The device driver initializes the device at this time.
You use the iospace parameters to pass in the exact bus addresses that correspond to this device. Up to three address space ranges can be passed to the driver. This does not restrict the device—it can use other ranges of addresses, but the device driver has to deduce their addresses from other information. The device driver typically uses this data to set up PIO maps (see “Mapping PIO Addresses”).
The kernel provides services for mapping the EISA bus into the kernel virtual address space for PIO or DMA, and for transferring data using these maps. Two types of DMA are supported, Bus-master DMA and Slave DMA.
A PIO map is a system object that represents the mapping of a location in kernel virtual memory to some range of addresses on a VME or EISA bus. After creating a PIO map, a device driver can use it in the following ways:
Extract a specific kernel virtual address that represents the device. This address can be used to load or store data, or it can be mapped that into user process space.
Copy data between the device and memory without learning the specific kernel addresses involved.
Perform bus read-modify-write cycles to apply Boolean operators to device data.
The functions used with PIO maps are summarized in Table 18-1.
Table 18-1. Functions to Create and Use PIO Maps
|
| Can Sleep |
|
|---|---|---|---|
pio_mapalloc(D3) | pio.h & types.h | Y | Allocate a PIO map. |
pio_mapfree(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | Free a PIO map. |
pio_badaddr(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | Check for bus error when reading an address. |
pio_wbadaddr(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | Check for bus error when writing to an address. |
pio_mapaddr(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | Convert a bus address to a virtual address. |
pio_bcopyin(D3) | pio.h & types.h | Y | Copy data from a bus address to kernel's virtual space. |
pio_bcopyout(D3) | pio.h & types.h | Y | Copy data from kernel's virtual space to a bus address. |
pio_andb_rmw(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | Byte read-AND-write cycle. |
pio_andh_rmw(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | 16-bit read-AND-write cycle. |
pio_andw_rmw(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | 32-bit read-AND-write cycle. |
pio_orb_rmw(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | Byte read-OR-write cycle. |
pio_orh_rmw(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | 16-bit read-OR-write cycle. |
pio_orw_rmw(D3) | pio.h & types.h | N | 32-bit read-OR-write cycle. |
A kernel-level device driver creates a PIO map by calling pio_mapalloc(). This function performs memory allocation and so can sleep. PIO maps are typically created in the pfxedtinit() entry point, where the driver first learns about the device addresses from the contents of the edt_t structure (see “Entry Point edtinit()” in Chapter 7).
The parameters to pio_mapalloc() describe the range of addresses that can be mapped in terms of
the bus type, in this case ADAP_EISA from sys/edt.h
the bus number, when more than one bus is supported
the address space, using constants such as PIOMAP_EISA_IO from sys/pio.h
the starting bus address and a length
This call also specifies a “fixed” or “unfixed” map. This distinction applies only to VME maps. An EISA map is always a fixed map.
A call to pio_mapfree() releases a PIO map. PIO maps created by a loadable driver must be released in the pfxunload() entry point (see “Entry Point unload()” in Chapter 7 and “Unloading” in Chapter 9).
The PIO map is created from the parameters that are passed. These are not validated by pio_mapalloc(). If there is any possibility that the mapped device is not installed, not active, or improperly configured, you should test the mapped address.
The pio_baddr() and pio_wbaddr() functions test the mapped address to see if it is usable.
From a fixed PIO map you can recover a kernel virtual address that corresponds to the first bus address in the map. The pio_mapaddr() function is used for this.
You can use this address to load or store data into device registers. In the pfxmap() entry point (see “Concepts and Use of mmap()” in Chapter 7), you can use this address with the v_mapphys() function to map the range of device addresses into the address space of a user process.
You can apply a variety of kernel functions to any PIO map, fixed or unfixed. The pio_bcopyin() and pio_bcopyout() functions copy a range of data between memory and a PIO map. There is no performance advantage to using these functions, as compared to loading or storing to the mapped addresses, but their use makes the device driver code simpler and more readable.
The series of functions pio_andb_rmw() and pio_orb_rmw() perform a read-modify-write cycle. You can use them to set or clear bits in device registers. Read-modify-write cycles on the EISA bus are atomic operations to software only (see “EISA Locked Cycles”).
Before a kernel-level driver can field EISA interrupts, it must associate a handler with one of the IRQ levels. In order to perform DMA, the driver must allocate one of the DMA channels. The functions used for these purposes are summarized in Table 18-2.
Table 18-2. Functions for IRQ and Channel Allocation
Function | Header Files | Can Sleep | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
eisa_dmachan_alloc() | eisa.h & types.h | N | Allocate DMA channel. |
eisa_ivec_alloc() | eisa.h & types.h | N | Allocate IRQ and set triggering. |
eisa_ivec_set() | eisa.h & types.h | N | Associate handler to IRQ. |
The function eisa_ivec_alloc() allocates an available IRQ number from a set of acceptable numbers. Its prototype is
int eisa_ivec_alloc(uint_t adap,ushort_t mask,uchar_t trig); |
The arguments are as follows:
adap | The adapter number, always 0 in current systems. |
mask | A 16-bit mask containing a 1-bit for each IRQ level that is acceptable for this device. (For available IRQ levels, see “EISA Interrupts” .) |
trig | The triggering method used by the card, either EISA_EDGE_IRQ or EISA_LEVEL_IRQ from sys/eisa.h. |
ISA cards are usually hard-wired or jumpered to a particular IRQ, so that the mask argument contains a single bit. Some EISA cards can be programmed dynamically to use a selected IRQ; in that case mask contains a 1-bit for each IRQ the card can be programmed to use.
The function attempts to allocate an IRQ from the mask set that is not in use by any card. If all acceptable levels are in use, it allocates an IRQ that is already in use with the requested kind of triggering. In either case, it returns the number of the IRQ to be used.
In the event that all the IRQs requested are already in use with a conflicting type of triggering, the function returns -1.
After allocating an IRQ, the device driver programs the card (using PIO) to interrupt on that line.
The function eisa_ivec_set() associates a function in the device driver with an IRQ number. Its prototype is
int eisa_ivec_set(uint_t adap, int irq,
void (*e_intr)(long), long e_arg)
|
The parameters are as follows:
adap | The adapter number, always 0 in current systems. |
irq | The IRQ level to be monitored. |
e_intr | The address of the interrupt handling function to call. |
e_arg | An argument to pass to the function when called. |
When more than one device is allocated the same IRQ, the kernel calls all the interrupt functions associated with that IRQ. This means that an interrupt function must always verify, by testing device registers, that the interrupt was caused by its device.
The first call to eisa_ivec_set() for a given IRQ enables interrupts from that IRQ. Prior to the call, interrupts from that IRQ are ignored.
| Note: If you are working with both the VME and EISA interfaces, it is worth noting that the number and type of arguments of eisa_ivec_set() differ from those of vme_ivec_set(). |
| Note: There is no way to retract the association of an interrupt function with an IRQ. This means that if an EISA driver handles interrupts and is loadable, it must not support the pfxunload() entry point. An interrupt arriving after the driver had been unloaded would panic the system. |
The function eisa_dmachan_alloc() allocates one of the seven available DMA channels (channel 4 is reserved by the hardware) from a set of acceptable channels. The function's prototype is
int eisa_dmachan_alloc(uint_t adap, uchar_t dma_mask) |
The arguments are as follows:
adap | The adapter number, always 0 in current systems. |
dma_mask | An 8-bit mask containing 1-bits for the DMA channels that can be used by this device. |
The function allocates the channel in the requested set that is in use by the fewest devices. It is possible for a single channel to be requested by multiple devices. However, if the device can use any of several channels, it is likely that the device will be the only one using the channel whose number is returned. After allocating a channel number, the device driver programs the device to use that channel, if necessary.
Bus-master DMA is performed by an EISA card that has bus-master logic. The card generates the DMA bus cycles, and provides the target memory address to store or retrieve data.
The device driver sets up Bus-master DMA by programming the card with a target physical address and length of data. Some cards support scatter/gather operations, in which the card is programmed with a list of memory pages and their lengths, and the card transfers a stream of data across all of the pages. However, programming an EISA bus master card is a highly hardware-dependent operation. The cards vary widely in their capabilities and programming methods.
The key programming issue for a device driver is locating the target memory buffers in system memory, so as to be able to program the EISA card with correct physical memory addresses.
The kernel provides functions for mapping memory for DMA. The functions that operate on EISA DMA maps are summarized in Table 18-3.
Table 18-3. Functions That Operate on DMA Maps
Function | Header Files | Can Sleep | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
dma_map(D3) | dmamap.h & types.h & sema.h | N | Prepare DMA mapping. |
dma_mapaddr(D3) | dmamap.h & types.h & sema.h | N | Return the target physical address for a given map and address. |
dma_mapalloc(D3) | dmamap.h & types.h & sema.h | Y | Allocate a DMA map. |
dma_mapfree(D3) | dmamap.h & types.h & sema.h | N | Free a DMA map. |
A device driver allocates a DMA map using dma_mapalloc(). This is typically done in the pfxedtinit() entry point, provided that the maximum I/O size is known at that time (see “Entry Point edtinit()” in Chapter 7).
A DMA map is used prior to a DMA transfer into or out of a buffer in kernel virtual space. The function dma_map() takes a DMA map, a buffer address, and a length. It relates the buffer address to physical addresses for use in DMA, and returns the length mapped. The returned length is typically less than the length of the buffer. This is because, for EISA, the function does not support scatter/gather, so the mapping must stop at the first page boundary.
After calling dma_map(), the device driver calls dma_mapaddr() to get the physical address corresponding to the current map. This is the address that is programmed into the EISA bus master card as a target address for a segment of the transfer up to one page in size.
Repeated calls to dma_map() and dma_mapaddr() can be used to map successive pages, until the EISA card is loaded with as many transfer segment addresses as it supports.
In Slave DMA, an EISA card that does not have DMA logic is commanded by the EISA Interface Unit and 82350 chip set (see Figure 18-1) to perform a series of transfers into memory.
The kernel supplies a unique set of functions for managing Slave DMA, unrelated to the DMA functions for Bus-master DMA. The functions that operate on EISA DMA maps are summarized in Table 18-4.
Table 18-4. Functions for EISA DMA
Function | Header Files | Can Sleep | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
eisa_dma_disable(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | N | Disable recognition of hardware requests on a DMA channel. |
eisa_dma_enable(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | N | Enable recognition of hardware requests on a DMA channel. |
eisa_dma_free_buf(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | N | Free a previously allocated DMA buffer descriptor. |
eisa_dma_free_cb(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | N | Free a previously allocated DMA command block. |
eisa_dma_get_buf(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | Y | Allocate a DMA buffer descriptor. |
eisa_dma_get_cb(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | Y | Allocate a DMA command block. |
eisa_dma_prog(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | Y | Program a DMA operation for a subsequent software request. |
eisa_dma_stop(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | N | Stop software-initiated DMA operation and release channel. |
eisa_dma_swstart(D3) | eisa.h & types.h | Y | Initiate a DMA operation via software request. |
The EISA attachment hardware has many options for performing Slave DMA, and most of these options are reflected in the contents of the eisa_dma_cb and eisa_dma_buf data structures (see the eisa_dma_buf(D4) and eisa_dma_cb(D4) reference pages, in addition to the reference pages listed in Table 18-4). By setting appropriate values declared in sys/eisa.h into these structures, you can program most varieties of Slave DMA.
This section shows initialization code, and a complete EISA driver.
The code in Table 18-1 represents an outline of the pfxedtinit() entry point for a hypothetical EISA device, showing the allocation of a PIO map, an IRQ, and a DMA channel. The driver supports as many as four identical devices. It keeps information about them in an array of structures, einfo. Each entry to pfxedtinit() initializes one element of this array, as indexed by the ctlr value from the VECTOR statement.
An important point to note in the example below is that most of the arguments to pio_map_alloc() can simply be passed as the values from the edt_t received by the entry point.
Example 18-1. Sketch of EISA Initialization
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/edt.h>
#include <sys/pio.h>
#include <sys/eisa.h>
#include <sys/cmn_err.h>
#define MAX_DEVICE 4
/* Array of info structures about each device. A device
** that does not initialize OK ought to be marked, but
** no such logic is shown.
*/
struct edrv_info {
caddr_t e_addr[NBASE]; /* pio mapped addr per space */
int e_dmachan; /* dma chan in use */
} einfo[MAX_DEVICE];
#define CARD_ID 0x0163b30a /* mfr. ID */
#define IRQ_MASK 0x0018 /* acceptable IRQs */
#define DMACHAN_MASK 0x7a /* acceptable chans */
edrv_edtinit(edt_t *e)
{
int iospace; /* index over iospace array */
int eirq; /* allocated IRQ # */
int edma_chan; /* allocated chan # */
struct edrv_info *einf; /* -> einfo[n] */
piomap_t *pmap;
if (e->e_ctlr < MAX_DEVICE)
einf = &einfo[e->e_ctlr];
else
{ /* unknown device, nowhere to put info */
cmn_err(CE_WARN,"devno too large:%d",e->e_ctlr);
return;
}
/* for each nonempty iospace parameter,
** set up a PIO map and save the kv address.
*/
for (iospace = 0; iospace < NBASE; iospace++) {
if (!e->e_space[iospace].ios_iopaddr)
einf->e_addr[iospace] = 0; /* note no addr */
pmap = pio_mapalloc( /* make a PIO map */
e->e_bus_type, /* pass bus type given */
e->e_adap, /* pass adapter # given */
&e->e_space[iospace], /* given iospace too */
PIOMAP_FIXED, /* always fixed for EISA */
"edrv");
einf->e_addr[iospace] = pio_mapaddr(pmap,
e->e_space[iospace].ios_iopaddr);
}
/* Set up an edge-triggered IRQ for this device.
** Associate it with our interrupt entry point.
** There is no need to remember the assigned IRQ.
*/
eirq = eisa_ivec_alloc(e->e_adap,IRQ_MASK,EISA_EDGE_IRQ);
if (eirq < 0) {
cmn_err(CE_WARN,
"edrv: ctlr %d could not allocate IRQ\n”,
e->e_ctlr);
/* should mark einfo unusable */
return;
}
eisa_ivec_set(e->e_adap, eirq, edrv_intr, e->e_ctlr);
/* Allocate a DMA Channel for this device and note
** the number in the device info array.
*/
edma_chan = eisa_dmachan_alloc(e->e_adap,DMACHAN_MASK);
if (edma_chan < 0) {
cmn_err(CE_WARN,
"edrv: ctlr %d could not allocate DMA Chan\n",
e->e_ctlr);
/* should mark einfo unusable */
return;
}
einf->e_dmachan = edma_chan;
}
|
The code in this section displays a complete character device driver for an EISA card, the Roland RAP-10 synthesizer. This inexpensive synthesizer card can be installed in an Indigo2 and driven by a program through this device driver.
Example 18-6 displays the code of the driver itself.
Example 18-2 displays the descriptive file to be placed in /var/sysgen/master.d to describe the driver.
Example 18-3 displays the configuration file to be placed in /var/sysgen/system to enable loading the driver.
Example 18-4 displays a shell script to install the driver.
Example 18-5 contains a test program to operate the synthesizer.
Example 18-2. Master File /var/sysgen/rap for RAP-10 Driver
* * rap - Roland RAP-10 Musical Board * * $Revision: 1.17 $ * *FLAG PREFIX SOFT #DEV DEPENDENCIES c rap 61 - $$$
Example 18-3. Configuration File /var/sysgen/rap.sm for RAP-10 Driver
VECTOR: bustype=EISA module=rap ctlr=0 adapter=0 iospace=(EISAIO,0x330,16) probe_space=(EISAIO,0x330,1) |
Example 18-4. Installation Script for RAP-10 Driver
#!/bin/csh if [ `whoami`!= “root” ] then echo “You must be root to run this script.\n” exit 1 fi echo “cp rap.o /var/sysgen/boot/rap.o\n” cp rap.o /var/sysgen/boot/rap.o echo “cp rap.master /var/sysgen/master.d/rap\n” cp rap.master /var/sysgen/master.d/rap echo “cp rap.sm /var/sysgen/system/rap.sm” cp rap.sm /var/sysgen/system/rap.sm echo “mknod /dev/rap c 62 0\n” mknod /dev/rap c 62 0 echo “Make a new kernel anytime by typing: autoconfig -f -v\n” |
Example 18-5. Program to Test RAP-10 Driver
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include “rap.h”
/*
* record.c
*
* This program plays song from a previuosly recorded file
* using RAP-10 board.
*
*/
#define BUF_SIZE 4096
#define FILE_HDR “RAP-10 WAVE FILE”
#define RAP_FILE “/dev/rap”
#define MAX_BUF 10
#define FOREVER for(;;)
uchar_t buf[BUF_SIZE];
uchar_t *fname;
void endProg( int );
main (int argc, char **argv)
{
register int fd, rapfd, bytes;
if ( argc <= 1 ) {
printf (“play: Usage: play <file_name>\n”);
exit(0);
}
fname = argv[1];
printf (“play: opening file %s\n”, fname);
fd = open (fname, O_RDONLY);
if ( fd == -1 ) {
printf (“play: Cannot create file, errno = %d\n”, errno);
close(rapfd);
exit(0);
}
printf (“play: Checking RAP-10 File ID\n”);
if ( read(fd, buf, strlen(FILE_HDR)) <= 0 ) {
printf (“play: Could not read the file ID, errno = %d\n”,
errno);
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
if ( strcmp(buf, FILE_HDR) ) {
printf (“play: File is not a RAP file\n”);
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
printf (“play: opening RAP card\n”);
rapfd = open (RAP_FILE, O_WRONLY);
if ( rapfd <= 0 ) {
printf (“play: Cannot open RAP card, errno = %d\n”,
errno);
exit(0);
}
printf (“play: Playing ..please wait\n”);
/* ignore Interrupt */
sigset (SIGINT, SIG_IGN );
FOREVER {
bytes = read(fd, buf, BUF_SIZE);
if ( bytes < 0 ) {
printf (“play: error reading data, errno = %d”,
errno);
close(fd);
close(rapfd);
exit(0);
}
if ( bytes == 0 )
break;
bytes = write(rapfd, buf, BUF_SIZE);
if ( bytes <= 0 ) {
printf (“play: Cannot read from RAP, errno = %d\n”,
errno);
close (rapfd);
close (fd);
exit(0);
}
}
printf (“play: waiting for Play to End\n”);
if ( ioctl (rapfd, RAPIOCTL_END_PLAY) ) {
printf (“play: Ioctl error %d”, errno );
}
else printf (“play: Song succesfully played\n”);
close(rapfd);
close (fd);
}
|
Example 18-6. Complete EISA Character Driver for RAP-10
/*****************************************************************************
*
* Roland RAP-10 Music Card Device Driver for Eisa Bus
* ---------------------------------------------------
*
* INTRODUCTION:
* -------------
* This file contains the device driver for Roland RAP-10
* Music Card. Currently it contains necessary routines to Record and
* Playback a Wave file. The MIDI Implementation is to be defined and
* implemented at later time.
*
* DESIGN OVERVIEW:
* ----------------
* We will use DMA for wave data movements. At any given time, the card
* can be either playing or recording and both operations are not allowed.
* Also no more than one process at a time can access the card.
*
* Circular Buffers:
* -----------------
* Since DMA operation is performed independently of the processor,
* we will buffer the user's data and release the user's process to
* do other things (i.e. preparing more data). Internally we use a
* circular queue (rwQue) to store the data to be played or recorded.
* Each entry in this queue is of the type rwBuf_t where the data will
* be stored. Each entry can store up to RW_BUF_SIZE bytes of data.
* At the init time, we try to allocate two DMA channels for the card:
* Channel 5 and 6. If we can only allocate Channel 5, we will use the
* card in Mono mode, otherwise, we will use it as Stereo. DMA has two
* buffers of its own: dmaRigh[] and dmaLeft[] for each Channel. For
* Stereo play, the data user provides us is of the format:
*
* <Left Byte><Right Byte><Left Byte><Right Byte>.....
*
* So for playing, we have to move all Left_Bytes to dmaLeft buffer
* and all Right_Bytes to the dmaRight buffer (in Stereo mode only).
* In mono mode, we will use dmaLeft[] buffer and all the user's data
* are moved to dmaLeft[].
*
* The basic operation of the Card are as follow:
*
* Playing:
* --------
* For playing wave data, the user must first open the card through
* open() system call.The call comes to us as rapopen(). This
* routine resets all global values, states and counters, prepares
* necessary DMA structures for each channel, disables RAP-10
* interrupts and establishes this process as the owner of the card.
*
* The user provides us with the wave data by issuing write()
* system calls. This call comes to us as rapwrite(). We will
* move the data from user's address space into an empty rwQue[]
* entry and will retrun so that the user can issue another call.
* If there is no DMA going, we will start one and the data will
* start to be moved to the Card to be played.
* The user can issue as many write() as necessary. The playing
* operation will be done by either closing the card or issuing
* an Ioctl call. Issuing Ioctl, will leave this process as owner
* still while closing the card will release the card.
*
* Recording:
* ----------
* Assuming that the user has opened the card and is the current
* owner, user will issue read() system call. The call comes to
* us as rapread(). If no DMA Record is going on, we will start
* one. We will move data from rwQue[] entries (as they are filled)
* to user's address space. The recording is done either by a
* close() or ioctl() call.
*
* DMA Starting:
* -------------
* For Playing, we will start DMA when we have a full circular buffer.
* This is done so that we have enough data available for a fast DMA
* operation to be busy with. For recording, we will start DMA
* immediatly.
*
* Interrupts:
* -----------
* For each DMA transfer, we will receive two interrupts: One when 1st
* half the buffer is transfered, one when 2nd half of the buffer is
* transfered. We must fill the half that has just been transfered with
* fresh data. Note that in Stereo mode, there are two DMA operation
* going. So when we receive Interrupt for one DMA, we must wait for the
* exact interrupt from the other DMA and service both DMA's half buffers.
*
* Card Address and IRQ
* --------------------
* We will use the default bus address of 0x330 and IRQ 5. Change in
* bus address should also be reflected in /var/sysgen/system/rap.sm
* file. Changes in IRQ should be reflected in the source code and
* the program must be recomplied.
*
* ISSUES:
* -------
* 1. The DMA processing and transfer of data from/to user's buffer
* are independent of each other. When we are servicing the
* one half of the dma buffer that just been transfered, there is
* no guarantee that we can fill that half of the buffer BEFORE
* dma is done with the other half. In this case, dma plays the
* fist half of buffer WHILE we are writing into it.
*
* 2. Currently eisa_dma_disable() routine does not actually
* releases the Dma channels. This is the reason why we access
* the Dma channel table (e_ch[]) ourselves and release the
* channel.
*
* 3. Somehow because of number 2, the Play program cannot be
* stopped with a Ctrl-C. In Play program this signal is
* explicitly ignored. Trapping a Ctrl-C causes a kernel panic.
* Once we have a workable eisa_dma_disable(), this problem will
* be resolved.
*
* TECHNICAL REFERENCES:
* ---------------------
* Roland RAP-10 Technical Reference and Programmer's Guide, Ver. 1.1
* IRIX Device Driver Programming Guide
* IRIX Device Driver Reference Pages.
* Intel 82357 Preliminary Reference, Section: 3.7.8 Mode Register (pp: 223)
*
******************************************************************************
*** ***
*** Copyright 1994, Silicon Graphics Inc., Mountain View, CA. ***
*** ***
******************************************************************************
*/
#include “sys/types.h”
#include “sys/file.h”
#include “sys/errno.h”
#include “sys/open.h”
#include “sys/conf.h”
#include “sys/cmn_err.h”
#include “sys/debug.h”
#include “sys/param.h”
#include “sys/edt.h”
#include “sys/pio.h”
#include “sys/uio.h”
#include “sys/proc.h”
#include “sys/user.h”
#include “sys/eisa.h”
#include “sys/sema.h”
#include “sys/buf.h”
#include “sys/cred.h”
#include “sys/kmem.h”
#include “sys/ddi.h”
#include “./rap.h”
/*
* Macros to Read/Write 8 and 16-bit values from an address
*/
#define OUTB(addr, b) ( *(volatile uchar_t *)(addr) = (b) )
#define INPB(addr) ( *(volatile uchar_t *)(addr) )
#define OUTW(addr, w) ( *(volatile ushort_t *)(addr) = (w) )
#define INPW(addr) ( *(volatile ushort_t *)(addr) )
/*
* Raising and lowering CPU interrupt
*/
#define LOCK() spl5()
#define UNLOCK(s) splx(s)
#define FROM_INTR 1
#define FROM_USR 0
#define User_pid u.u_procp->p_pid
/*
* IRQ and DMA channels we need.
*
*/
#define IRQ_MASK 0x0020
#define DMAC_CH5 0x20 /* DMA Channel 5 */
#define DMAC_CH6 0x40 /* DMA Channel 6 */
/*=======================================*
* MIDI and RAP Registers *
*=======================================*
*
* The following is a description of RAP-10 registers. The same
* names used throughout this program. Some of these registers are
* 8-bit and some are 16-bit long.
*
* mdrd: MIDI Receive Data
* mdtd: MIDI Transmit Data
* mdst: MIDI Status
* mdcm: MIDI Command
* pwmd: Pulse Width Modulation Data
* timm: Timer MSB data
* gpcm: GPCC Command
* dtci: DMA Transfer Count Buffer Interrupt Status
* adcm: GPCC Analog to Digital Command
* dacm: D/A Command and DMA Transfer Configuration
* gpis: GPCC Interrupt Status
* gpdi: GPCC DMA/Interrupt Enable
* gpst: GPCC Status
* dad0: Digital to Analog Data Channel 0
* addt: A/D Data Transfer
* dad1: Digital to Analog Data Channel 1
* timd: Timer Data
* cmp0: Compare Register Channel 0
* dtcd: DMA Transfer Count Data
* cmp1: Compare Register Channel 1
*
* These defines indicate the offsets of the above registers
* from the Drive's base address:
*/
#define MDRD 0x0
#define MDTD 0x0
#define MDST 0x1
#define MDCM 0x1
#define PWMD 0x2
#define TIMM 0x3
#define GPCM 0x3
#define DTCI 0x4
#define ADCM 0x4
#define DACM 0x5
#define GPIS 0x6
#define GPDI 0x6
#define GPST 0x8
#define DAD0 0x8
#define ADDT 0xa
#define DAD1 0xa
#define TIMD 0xc
#define CMP0 0xc
#define DTCD 0xe
#define CMP1 0xe
typedef struct rapReg {
uchar_t mdrd;
uchar_t mdtd;
uchar_t mdst;
uchar_t mdcm;
uchar_t pwmd;
uchar_t timm;
uchar_t gpcm;
uchar_t dtci;
uchar_t adcm;
uchar_t dacm;
ushort_t gpis;
ushort_t gpdi;
ushort_t gpst;
ushort_t dad0;
ushort_t addt;
ushort_t dad1;
ushort_t timd;
ushort_t cmp0;
ushort_t dtcd;
ushort_t cmp1;
} rapReg_t;
/*==========================================================*
* dtct (DMA Transfer Count) *
*==========================================================*/
#define DTCD_DRQ0 0x00FF /* DRQ 0 bits (0-7) */
#define DTCD_DRQ1 0xFF00 /* DRQ 1 bits (8-15) */
/*==========================================================*
* gpst (GPCC Status) *
*==========================================================*/
#define GPST_PWM2 0x0800 /* PWM2 Busy (0=Write Enable, 1=Busy) */
#define GPST_PWM1 0x0400 /* PWM1 Busy (0=Write Enable, 1=Busy) */
#define GPST_PWM0 0x0200 /* PWM0 Busy (0=Write Enable, 1=Busy) */
#define GPST_EPB 0x0100 /* EP Convertor Busy (0=Write Enable, 1=Busy) */
#define GPST_GP1 0x0080 /* GP-chip, Ch 1 Acess (1 = Access) */
#define GPST_GP0 0x0040 /* GP-chip, Ch 0 Acess (1 = Access) */
#define GPST_MTE 0x0020 /* MIDI Tx Enable (0=Tx_Fifo buff full) */
#define GPST_ORE 0x0010 /* MIDI Overrun Error (1 = error) */
#define GPST_FE 0x0008 /* MIDI Framing Error (1 = error) */
#define GPST_ADE 0x0004 /* A/D Error (1 = error) */
#define GPST_DE1 0x0002 /* D/A Ch 1 Write Error (1 = error) */
#define GPST_DE0 0x0001 /* D/A Ch 0 Write Error (1 = error) */
/*==========================================================*
* gpdi (GPCC DMA/Interrupt Enable (pp: 4-18) *
*==========================================================*/
#define GPDI_ITC 0x8000 /* DMA Transfer Cnt Match (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_DC2 0x4000 /* DMA Chann. Assignment, bit2 (pp:4-18) */
#define GPDI_DC1 0x2000 /* DMA Chann. Assignment, bit1 (pp:4-18) */
#define GPDI_DC0 0x1000 /* DMA Chann. Assignment, bit0 (pp:4-18) */
#define GPDI_DT1 0x0800 /* DMA Trans. Mode, bit:1 (pp: 4-18) */
#define GPDI_DT0 0x0400 /* DMA Trans. Mode, bit:0 (pp: 4-18) */
#define GPDI_OVF 0x0200 /* Free Run.Cntr (FCR) Ov.Flow (0=Disable)*/
#define GPDI_TC1 0x0100 /* Timer 1 Compare Match (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_TC0 0x0080 /* Timer 0 Compare Match (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_RXD 0x0040 /* MIDI Data Read Request (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_TXD 0x0020 /* MIDI Tx_fifo Buf Empty (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_ADD 0x0010 /* A/D Data Ready (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_DN1 0x0008 /* D/A Ch1 Note ON Ready (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_DN0 0x0004 /* D/A Ch0 Note ON Ready (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_DQ1 0x0002 /* D/A Ch1 Data Request (0=Disable) */
#define GPDI_DQ0 0x0001 /* D/A Ch0 Data Request (0=Disable) */
/*==========================================================*
* gpis (GPCC Interrupt Status .. pp: 4-16) *
*==========================================================*/
#define GPIS_ITC 0x8000 /* DMA Transfer Count Match */
#define GPIS_JSD 0x0400 /* Joystick Data Ready */
#define GPIS_OVF 0x0200 /* Free Running Countr Overflow */
#define GPIS_TC1 0x0100 /* Timer1 Compare Match */
#define GPIS_TC0 0x0080 /* Timer0 Compare Match */
#define GPIS_RXD 0x0040 /* MIDI Data Read Request */
#define GPIS_TXD 0x0020 /* MIDI Tx_fifo Buf. Empty */
#define GPIS_ADD 0x0010 /* A/D Data Ready */
#define GPIS_DN1 0x0008 /* D/A Ch1 Note ON Ready */
#define GPIS_DN0 0x0004 /* D/A Ch0 Note ON Ready */
#define GPIS_DQ1 0x0002 /* D/A Ch1 Data Request */
#define GPIS_DQ0 0x0001 /* D/A Ch0 Data Request */
/*===================================================================*
* dacm (Digital To Analogue Cmd and DMA Transfer Config) *
*===================================================================*/
#define DACM_SCC 0x80 /* DMA Size Cmp. Cnt (0=in Sample, 1=in Bytes)*/
#define DACM_TS2 0x40 /* DMA Trnsfr Size, bit 2 (pp: 4-14) */
#define DACM_TS1 0x20 /* DMA Trnsfr Size, bit 1 (pp: 4-14) */
#define DACM_TS0 0x10 /* DMA Trnsfr Size, bit 0 (pp: 4-14) */
#define DACM_DL1 0x08 /* Ch1 DA Data Len (0=8 bit, 1=17 bit) */
#define DACM_DL0 0x04 /* Ch0 DA Data Len (0=8 bit, 1=17 bit) */
#define DACM_DS1 0x02 /* Ch1 DA Convrsion (0=Stop, 1=Start) */
#define DACM_DS0 0x01 /* Ch0 DA Convrsion (0=Stop, 1=Start) */
/*=====================================================*
* adcm ( GPCC AD Command ) *
*=====================================================*/
#define ADCM_MON 0x40 /* Monitor MIC (0=Monitor Off) */
#define ADCM_GIN 0x20 /* Gain Input (0=Line, 1=Mic) */
#define ADCM_AF1 0x10 /* Analog Freq Selection bit 1 (pp: 4-13) */
#define ADCM_AF0 0x08 /* Analog Freq Selection bit 0 (pp: 4-13) */
#define ADCM_ADL 0x04 /* Analog Data Length (0=8, 1=16) */
#define ADCM_ADM 0x02 /* Analog Data Conv. Mode (0=Mono,1=Stereo) */
#define ADCM_ADS 0x01 /* Analog Data Conv. Start(0=Stop,1=Start) */
/*=====================================================*
* dtci ( DMA Trans.Count Buf Intr. Stat *
*=====================================================*/
#define DTCI_BF1 0x08 /* DMA DRQ1 buff full (1 = full) */
#define DTCI_BH1 0x04 /* DMA DRQ1 buff half (1 = full) */
#define DTCI_BF0 0x02 /* DMA DRQ0 buff full (1 = full) */
#define DTCI_BH0 0x01 /* DMA DRQ0 buff half (1 = full) */
/*========================================*
* gpcm ( GPCC Command ) *
*========================================*/
#define GPCM_RST 0x80 /* Reset bit */
#define GPCM_PWM2 0x10 /* Select PWM channel 2 */
#define GPCM_PWM1 0x08 /* Select PWM channel 1 */
#define GPCM_PWM0 0x04 /* Select PWM channel 0 */
#define GPCM_FRCM 0x02 /* Free Run. Counter (1=Start) */
#define GPCM_MTT 0x01 /* MIDI Timed Trans */
/* ( 1 = Timer INT enabled ) */
/*======================================*
* timm (Timer MSB data) *
*======================================*/
#define TIMM_FRC 0x04 /* Free Running Counter Bit 16 */
#define TIMM_CR1 0x02 /* Compare Reg 1 Bit 16 */
#define TIMM_CR0 0x01 /* Compare Reg 0 Bit 16 */
/*===================================*
* mdcm (MIDI Command) *
*===================================*/
#define MDCM_UART 0x3f /* UART mode */
#define MDCM_MPU 0xff /* MPU Reset */
#define MDCM_VERSION 0xac /* Version */
#define MDCM_REVISION 0xad /* Revision */
/*===================================*
* mdst (MIDI Status) *
*===================================*/
#define MDST_DSR 0x80 /* DSR = 0 if ready */
#define MDST_DDR 0x40 /* DDR = 0 if ready */
/*====================================*
* RAP Card Info *
*====================================*
*
* These are the information regarding the RAP Card.
* The info being tracked are:
*
* ci_state: Our state (Installed, Opened, Playing, Recording)
* ci_pid: PID of process opened us.
* ci_addr[]: EISA Addresses
* ci_irq: EISA Interrupt number we use
* ci_ctl: Controller number we save from edt struct
* ci_adap: Adaptor number we save from edt struct.
* ci_dmaCh6: DMA Channel 6
* ci_dmaCh5: DMA Channel 5
* ci_dmaBuf6: EISA DMA Buffer struct for Channel 6
* ci_dmaBuf5: EISA DMA Buffer struct for Channel 5
* ci_dmaCb6: EISA DMA Control Block for Channel 6
* ci_dmaCb5: EISA DMA Control Block for Channel 5
* di_state: DMA buffers state (Idle, Progress)
* di_idx: Current rwQue[] entry being used.
* di_ptr: Address in rwQue buffer
* di_which: Which half of DMA buffer (0=1st half, 1=2nd Half)
* di_bh: Total DMA Buffer Half (BH) Interrupt received.
* di_bf: Total DMA Buffer Full (BF) Interrupt received.
* ri_state: State of Circular buffer (Wanted_Empty, etc.)
* ri_free: Total Free entries in rwQue[]
* ri_full: Total Full entries in rwQue[]
* ri_idx: Current rwBuf for Read/Write
* ri_tout; =1 if Timed out on read/write
* ri_note; number of Note_On received
* ri_ptr: Pointer in current rwBuf
*/
typedef struct eisa_dma_buf dmaBuf_t;
typedef struct eisa_dma_cb dmaCb_t;
typedef struct cardInfo_s {
/* Card Installation Info */
ushort_t ci_state;
pid_t ci_pid;
caddr_t ci_addr[NBASE];
int ci_irq;
int ci_ctl;
int ci_adap;
int ci_dmaCh6;
int ci_dmaCh5;
dmaBuf_t *ci_dmaBuf6;
dmaBuf_t *ci_dmaBuf5;
dmaCb_t *ci_dmaCb6;
dmaCb_t *ci_dmaCb5;
/* DMA Buffer Information data */
uchar_t di_state;
short di_idx;
uchar_t di_which;
caddr_t di_ptr;
uchar_t di_bh;
uchar_t di_bf;
/* Circular buffer Information data */
uchar_t ri_state;
short ri_free;
short ri_full;
short ri_idx;
uchar_t ri_tout;
uchar_t ri_note;
caddr_t ri_ptr;
} cardInfo_t;
/* ci_state values */
#define CARD_INSTALLED 0x0001
#define CARD_STEREO 0x0002
#define CARD_OPENED 0x0004
#define CARD_PLAYING 0x0010
#define CARD_RECORDING 0x0020
/* di_state values */
#define DI_DMA_IDLE 0x00
#define DI_DMA_PLAYING 0x01
#define DI_DMA_RECORDING 0x02
#define DI_DMA_END_PLAY 0x04
#define DI_DMA_END_RECORD 0x08
/* ri_state values */
#define RI_WANTED_EMPTY 0x01
/*====================================*
* Read/Write Circular Buffers *
*====================================*
* This is the description of our circular buffers used
* to store D/A and A/D values. D/A values are stored from
* user's buffer and then moved to DMA buffers. A/D data is
* moved from DMA buffers to these buffers and then moved
* to user's buffer. The fields are as follow:
* rw_state: buffer state (Empty, Busy, Full)
* rw_idx: Index of this buffer in rwQue[];
* rw_count: Total bytes in the buffer
* rw_buf[]: The buffer itself.
* RW_MIN_FULL: We will start a D/A DMA when we have this many
* full buffer on hand. This is done so that we can
* provide enough full buffers for DMA to process.
*/
#define RW_BUF_SIZE 8192
#define RW_BUF_COUNT 20
#define RW_MIN_FULL 1
#define RW_TIMEOUT 1600
typedef struct rwBuf_s {
uchar_t rw_state;
short rw_idx;
int rw_count;
uchar_t rw_buf[RW_BUF_SIZE];
} rwBuf_t;
/* rw_state values */
#define RW_EMPTY 0x00 /* used as parameter only */
#define RW_FULL 0x01
#define RW_WANTED_FULL 0x02
#define RW_WANTED_EMPTY 0x04
/*==================================*
* Global values *
*==================================*/
#define DMA_BUF_SIZE 8192
#define DMA_HALF_SIZE 4096
int rapdevflag = 0;
static cardInfo_t cardInfo;
static caddr_t dmaRight;
static caddr_t dmaLeft;
static paddr_t dmaRightPhys;
static paddr_t dmaLeftPhys;
static rwBuf_t rwQue[RW_BUF_COUNT];
static caddr_t eisa_addr;
/*
* Eisam Dma Channel semaphores..shoule be removed when
* proper way of releasing channels found
*/
extern struct eisa_ch_state {
sema_t chan_sem; /* inuse semaphore for each channel */
sema_t dma_sem; /* dma completion semaphore */
struct eisa_dma_buf *cur_buf; /* current eisa_dma_buf being dma'ed */
struct eisa_dma_cb *cur_cb; /* ptr to current command block */
int count;
} e_ch[];
/*=========================================*
* Driver Entry routines Data *
*=========================================*/
int rapopen ( dev_t *, int, int, cred_t * );
int rapread ( dev_t, uio_t *, cred_t * );
int rapwrite ( dev_t, uio_t *, cred_t * );
int rapclose ( dev_t, int, int, cred_t * );
void rapedtinit ( struct edt * );
void rapintr ( int );
int rapioctl (dev_t, int, void *, int, cred_t *, int *);
/*=======================================*
* Misc and Internal routines *
*=======================================*/
static void rapDisInt (cardInfo_t *);
static int rapGetDma( dmaBuf_t **, dmaCb_t **, int );
static int rapClose(uchar_t);
static short rapGetNextEmpty (short, uchar_t);
static short rapGetNextFull (short, uchar_t);
static void rapPrepEisa( dmaBuf_t *, dmaCb_t *, uchar_t, paddr_t);
static int rapStart(uchar_t);
static void rapStop(uchar_t);
static void rapStartDA();
static void rapStartAD();
static void rapBufToDma( int );
static void rapDmaToBuf( int );
static void rapMarkBuf(rwBuf_t *, cardInfo_t *, uchar_t);
static int rapKernMem(uchar_t);
static void rapSetAutoInit(cardInfo_t *, uchar_t);
static void rapTimeOut( void *);
static void rapNoteOn(cardInfo_t *, ushort_t );
static void rapNoteOff(cardInfo_t *);
static void rapZeroDma(cardInfo_t *, int);
static void rapReleaseDma (cardInfo_t *);
/*************************************************************************
* r a p e d t i n i t
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapedtint
* Purpose: Initializes the driver. Called once for each controller.
* Called only once.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
void
rapedtinit ( struct edt *e )
{
int ctl, iospace, dmac, eirq;
cardInfo_t *ci;
piomap_t *pmap;
iospace_t eisa_io;
ci = &cardInfo;
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapedtinit: Installing RAP board.”);
bzero ((void *)ci, sizeof(cardInfo_t) );
dmaRight = dmaLeft = (caddr_t)NULL;
ci->ci_ctl = e->e_ctlr;
ci->ci_adap = e->e_adap;
/*
* Get the base address of Eisa bus (for rapSetAutoInit)
*/
bzero (&eisa_io, sizeof(iospace_t));
eisa_io.ios_iopaddr = 0;
eisa_io.ios_size = 1000;
pmap = pio_mapalloc (e->e_bus_type, 0, &eisa_io, PIOMAP_FIXED, “eisa”);
if ( pmap == (piomap_t *)NULL ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN, “rapedtinit: Cannot get Eisa bus address”);
return;
}
eisa_addr = pio_mapaddr (pmap, eisa_io.ios_iopaddr);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapedtinit: Eisa base address = %x”, eisa_addr);
#endif
/*===================================================*
* map EISA IO/Memory addresses for RAP-10 card *
*===================================================*/
for ( iospace = 0; iospace < NBASE; iospace++ ) {
/* any address to map ? */
if ( !e->e_space[iospace].ios_iopaddr )
continue;
pmap = pio_mapalloc ( e->e_bus_type, e->e_adap,
&e->e_space[iospace],
PIOMAP_FIXED, “rap10” );
ci->ci_addr[iospace] = pio_mapaddr ( pmap,
e->e_space[iospace].ios_iopaddr );
}
/* is Card still there ? */
if ( badaddr(ci->ci_addr[0], 1) ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN, “rapedtinit: RAP board not installed.”);
return;
}
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapedtinit: First Load..allocating IRQ”);
#endif
eirq = eisa_ivec_alloc( e->e_adap, IRQ_MASK, EISA_EDGE_IRQ );
if ( eirq < 0 ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapedtinit: Could not allocate IRQ for RAP card.”);
return;
}
/* set Interrupt handler */
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapedtinit: Setting Interrupt Handler for IRQ %d”,
eirq);
#endif
if ( eisa_ivec_set(e->e_adap, eirq, rapintr, e->e_ctlr) == -1 ) {
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapedtinit: Could not set Interrupt handler for Irq %d”, eirq);
ci->ci_state = 0;
return;
}
ci->ci_irq = eirq;
/*======================================*
* DMA Channels Allocation *
*======================================*/
/* DMA channel 5 */
dmac = eisa_dmachan_alloc ( e->e_adap, DMAC_CH5 );
if ( dmac < 0 ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapedtinit: Could not allocate DMA Channel 5.”);
return;
}
ci->ci_dmaCh5 = dmac;
/* DMA channel 6 */
dmac = eisa_dmachan_alloc ( e->e_adap, DMAC_CH6 );
if ( dmac < 0 ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapedtinit: Could not allocate DMA Chann 6.”);
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapedtinit: RAP is initialized as Mono.”);
}
else {
ci->ci_dmaCh6 = dmac;
ci->ci_state |= CARD_STEREO;
}
/*==============================*
* DMA Buffer allocation *
*==============================*/
if ( rapKernMem (1) ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN, “rapedtinit: Did not install RAP-10.”);
return;
}
ci->ci_state |= CARD_INSTALLED;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapedtinit: RAP installed, Addr: %x, Irq: %d.”,
ci->ci_addr[0], ci->ci_irq );
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapedtinit: Init as %s, Dma 1 = %d, Dma 0 = %d”,
(ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO ? “Stereo”:”Mono”),
ci->ci_dmaCh5, ci->ci_dmaCh6);
#endif
return;
} /*** End rapedtinit ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p o p e n
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapopen
* Purpose: Opens the RAP board and initializes necessary data
* Returns: 0 = Success, or appropriate error number.
*************************************************************************/
int
rapopen ( dev_t *dev, int oflag, int otyp, cred_t *cred)
{
register int i;
cardInfo_t *ci;
rwBuf_t *rw;
dmaBuf_t *dmaB;
dmaCb_t *dmaC;
ci = &cardInfo;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapopen: Opening, Addr = %x, ci_state = %x”,
ci->ci_addr[0], ci->ci_state );
#endif
/*
* No card is installed or card is already opened
*/
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_INSTALLED) )
return (ENODEV);
if ( ci->ci_state & CARD_OPENED )
return (EBUSY);
/* Allocate DMA Buf and Cb for Channel 5 */
if ( ci->ci_dmaBuf5 == (dmaBuf_t *)NULL ) {
if ( rapGetDma(&dmaB, &dmaC, ci->ci_dmaCh5) ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,”rapopen: Could not allocate DMA Buf 5.”);
return (ENOMEM);
}
ci->ci_dmaBuf5 = dmaB;
ci->ci_dmaCb5 = dmaC;
}
/* if in stereo, do the same for Channel 6 */
if ( ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO ) {
if ( rapGetDma(&dmaB, &dmaC, ci->ci_dmaCh6) ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapopen: Could not allocate DMA Buf 6.”);
return (ENOMEM);
}
ci->ci_dmaBuf6 = dmaB;
ci->ci_dmaCb6 = dmaC;
}
/* Initialize Card Info structure */
ci->ri_idx = 0;
ci->di_idx = 0;
ci->ri_state = 0;
ci->di_state = 0;
ci->di_ptr = 0;
ci->ri_ptr = 0;
ci->ri_free = RW_BUF_COUNT;
ci->ri_full = 0;
ci->ci_state &= ~(CARD_PLAYING | CARD_RECORDING );
ci->ci_state |= CARD_OPENED;
ci->ci_pid = User_pid;
/* Initialize Circular Buffers */
for ( i = 0; i < RW_BUF_COUNT; i++ ) {
rw = &rwQue[i];
rw->rw_count = 0;
rw->rw_state = 0;
rw->rw_idx = i;
bzero (rw->rw_buf, RW_BUF_SIZE);
}
rapDisInt(ci);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapopen: Opened succesfully”);
#endif
return(0);
} /*** End rapopen ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p w r i t e
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapwrite
* Purpose: Write entry routine. This routine will transfer user's
* data to current or an empty entry in rwQue[] and starts
* DMA if none is going.
* Returns: 0 = Success, or errno
*************************************************************************/
int
rapwrite (dev_t dev, uio_t *uio, cred_t *cred)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
rwBuf_t *rw;
toid_t to_id;
int avail, size, totBytes, err, s;
ci = &cardInfo;
/*=========================*
* Error Checking *
*=========================*/
/* no card is installed */
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_INSTALLED) )
return (ENODEV);
/* card is not opened */
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_OPENED) )
return (EACCES);
/* we are not the owner */
if ( ci->ci_pid != User_pid )
return (EACCES);
/* is busy recording */
if ( ci->ci_state & CARD_RECORDING )
return (EACCES);
ci->ci_state |= CARD_PLAYING;
rw = &rwQue[ci->ri_idx];
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapwrite: %d bytes, buf = %d, rw_count = %d, free = %d, full = %d”,
uio->uio_resid, ci->ri_idx, rw->rw_count, ci->ri_free, ci->ri_full);
#endif
/* if it is full, wait till it is Empty */
s = LOCK();
if ( rw->rw_state & RW_FULL ) {
ci->ri_ptr = NULL;
ci->ri_tout = 0;
to_id = itimeout (rapTimeOut, rw, RW_TIMEOUT, plbase, 0, 0, 0);
while ( (rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) && !ci->ri_tout ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapwrite: waiting for buf %d to be Empty”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
rw->rw_state |= RW_WANTED_EMPTY;
if ( sleep (rw, PUSER | PCATCH) ) {
untimeout(to_id);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapwrite: Interrupted”);
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_EMPTY;
UNLOCK(s);
return (EINTR);
}
} /* while */
untimeout(to_id);
/* we timed out ..couldn't get the buffer */
if ( ci->ri_tout ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapwrite: Timed out”);
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_EMPTY;
UNLOCK(s);
return (EIO);
}
} /* if (rw->rw_state & RW_FULL */
UNLOCK(s);
/* adjuest the read/write address if necessary */
if ( ci->ri_ptr == NULL )
ci->ri_ptr = rw->rw_buf;
totBytes = uio->uio_resid;
while ( totBytes > 0 ) {
avail = RW_BUF_SIZE - rw->rw_count;
/* if this buffer is full, get next buffer */
if ( avail <= 0 ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapwrite: Buffer %d is Full now, rw_count = %d”,
rw->rw_idx, rw->rw_count);
#endif
s = LOCK();
rapMarkBuf(rw, ci, RW_FULL);
/* wake anyone wanted this buffer full */
if ( rw->rw_state & RW_WANTED_FULL ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,”rapwrite: Buffer %d is Wanted_Full”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_FULL;
wakeup(rw);
}
/*
* start DMA if none is going and we filled the
* entire buffers.
*/
if ( (ci->di_state == DI_DMA_IDLE) &&
(rw->rw_idx >= RW_MIN_FULL ) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,”rapwrite: Starting Play Dma”);
#endif
err = rapStart(DI_DMA_PLAYING);
if ( err ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapwrite: Could not start playing error %d”,err );
UNLOCK(s);
return(err);
}
}
/* get next empty buffer */
ci->ri_idx = rapGetNextEmpty(ci->ri_idx, FROM_USR);
rw = &rwQue[ci->ri_idx];
ci->ri_ptr = rw->rw_buf;
UNLOCK(s);
continue;
}
/* start filling this buffer */
size = (totBytes > avail ? avail: totBytes);
err = uiomove (ci->ri_ptr, size, UIO_WRITE, uio);
if ( err ) {
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapwrite: uiomov error %d”, err);
return(err);
}
rw->rw_count += size;
ci->ri_ptr += size;
totBytes = uio->uio_resid;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapwrite: Wrote %d to Buffer %d, Left = %d, rw_count = %d”,
size, rw->rw_idx, totBytes, rw->rw_count );
#endif
}
return (0);
} /*** end rapwrite ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p r e a d
*************************************************************************
*
* Name: rapread
*
* Purpose: Reads data from rwQue[] into user's buffer.
* This routine waits for current DMA operation to end
* and then starts a A/D Dma (recording). If A/D is already
* going then it simply moves data from current Full buffer
* into user's buffer. If buffer is not full, it waits for
* it to get full.
*
* Returns: 0 = Success, or errno.
*
*************************************************************************/
int
rapread (dev_t dev, uio_t *uio, cred_t *cred)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
rwBuf_t *rw;
toid_t to_id;
int avail, size, totBytes, err, s;
ci = &cardInfo;
/*===============================*
* Error Checking *
*===============================*/
/* card is not installed */
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_INSTALLED) )
return (ENODEV);
/* card is not opened */
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_OPENED) )
return (EACCES);
/* we do not own the card */
if ( ci->ci_pid != User_pid )
return (EACCES);
/* card is in middle of a Play operation */
if ( ci->ci_state & CARD_PLAYING )
return (EIO);
ci->ci_state |= CARD_RECORDING;
/* start a A/D Dma if none is going on */
if ( ci->di_state == DI_DMA_IDLE ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapread: Idle DMA. Starting one”);
#endif
if ( rapStart(DI_DMA_RECORDING) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapread: Could not start A/D”);
#endif
ci->ci_state &= ~CARD_RECORDING;
UNLOCK(s);
return (EIO);
}
}
/*
* get the buffer we should be using and
* wait for it to become Full
*/
rw = &rwQue[ci->ri_idx];
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapread: %d bytes, buf = %d, rw_count = %d, free = %d, full = %d”,
uio->uio_resid, ci->ri_idx, rw->rw_count, ci->ri_free, ci->ri_full);
#endif
s = LOCK();
if ( !(rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) ) {
ci->ri_ptr = NULL;
ci->ri_tout = 0;
to_id = itimeout (rapTimeOut, rw, RW_TIMEOUT, plbase, 0, 0, 0);
while ( !(rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) && !ci->ri_tout ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapread: wating for buf %d to become Full”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
rw->rw_state |= RW_WANTED_FULL;
if ( sleep (rw, PUSER | PCATCH) ) {
untimeout (to_id);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapread: Interrupted”);
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_FULL;
UNLOCK(s);
return(EINTR);
}
} /* while */
untimeout (to_id);
if ( ci->ri_tout ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapread: Timed out”);
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_FULL;
UNLOCK(s);
return (EIO);
}
} /* if !rw->rw_state & RW_FULL */
UNLOCK(s);
/* adjust read/write pointer if necessary */
if ( ci->ri_ptr == NULL )
ci->ri_ptr = rw->rw_buf;
/*===================================*
* Actual Read (Data movement) *
*===================================*/
totBytes = uio->uio_resid;
while ( totBytes > 0 ) {
avail = rw->rw_count;
/* if this buffer is Empty, get next Full buffer */
if ( avail <= 0 ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapread: Buffer %d is Empty now, rw_count = %d”,
rw->rw_idx, rw->rw_count );
#endif
s = LOCK();
rapMarkBuf(rw, ci, RW_EMPTY);
/* wake anyone wanted this buffer Empty */
if ( rw->rw_state & RW_WANTED_EMPTY ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,”rapread: Buffer %d is Wanted_Empty”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_FULL;
wakeup(rw);
}
/* get next Full buffer */
ci->ri_idx = rapGetNextFull(ci->ri_idx, FROM_USR);
rw = &rwQue[ci->ri_idx];
ci->ri_ptr = rw->rw_buf;
UNLOCK(s);
continue;
}
/* start filling this buffer */
size = (totBytes > avail ? avail: totBytes);
err = uiomove (ci->ri_ptr, size, UIO_READ, uio);
if ( err ) {
cmn_err (CE_PANIC, “rapread: uiomov error %d”, err);
return(err);
}
rw->rw_count -= size;
ci->ri_ptr += size;
totBytes = uio->uio_resid;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapread: Read %d, Buffer %d, Left = %d, rw_count = %d”,
size, rw->rw_idx, totBytes, rw->rw_count );
#endif
}
return (0);
} /*** End rapread ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p c l o s e
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapclose
* Purpose: closes connection to the card and makes it available
* for next process to open it.
* Returns: 0 = Success, or errno
*************************************************************************/
int
rapclose (dev_t dev, int flag, int otyp, cred_t *cred)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
ci = &cardInfo;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapclose: ci_state = %x, di_state = %x, full = %d, empty = %d”,
ci->ci_state, ci->di_state, ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free );
#endif
/*=========================*
* Error Checking *
*=========================*/
/* card is not installed */
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_INSTALLED) )
return (ENODEV);
/* card is not opened */
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_OPENED) )
return (EACCES);
/* we do not own the card */
if ( ci->ci_pid != User_pid )
return (EACCES);
return ( rapClose(1) );
}
/*************************************************************************
* r a p i n t r
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapintr
* Purpose: Interrupt handling routine
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
void
rapintr ( int ctl )
{
ushort_t gpis;
uchar_t dtci;
uchar_t stereo;
uchar_t totreq;
uchar_t playing;
uchar_t moveData;
cardInfo_t *ci;
caddr_t addr;
ci = &cardInfo;
addr = ci->ci_addr[0];
/*
* moveData: 0 = we should move data between Buf/DMA to DMA/Buf.
* totreq: In stereo, we have to wait for 2 BF or BH interrupt
* but in Mono we have to wait for only one.
* playing: 1 = Playing, 0= Recording.
*/
moveData = 0;
totreq = (ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO? 2:1); /* No. of Ints. we need */
playing = ci->ci_state & CARD_PLAYING;
gpis = INPW(addr+GPIS);
/*
* First, check for stray interrupts and ignore them
*/
if ( !(ci->ci_state & (CARD_PLAYING | CARD_RECORDING)) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: Stray interupt, gpis = %x, ci_state = %x”,
ci->ci_state );
#endif
return;
}
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapintr: New ..Gpis = %x”, gpis );
#endif
/**********************************
* DMA Buffers Half/Full *
**********************************/
while ( gpis & GPIS_ITC ) {
/* see which buffer is half/full */
dtci = INPB(addr+DTCI);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: Dma buffer status..Gpis = %x, Dtci = %x”, gpis, dtci);
#endif
if ( dtci & DTCI_BF0 )
ci->di_bf++;
if ( dtci & DTCI_BF1 )
ci->di_bf++;
if (dtci & DTCI_BH0 )
ci->di_bh++;
if (dtci & DTCI_BH1 )
ci->di_bh++;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapintr: di_bf = %d, di_bh = %d”,
ci->di_bf, ci->di_bh );
#endif
/* 1st half of dma needs service */
if ( ci->di_bh == totreq ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: DMA First_Half needs service”);
#endif
ci->di_bh = 0;
ci->di_which = 0; /* 1st half of DMA buffer */
moveData = 1;
}
/* 2nd half of dma needs service */
else if ( ci->di_bf == totreq ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: DMA Second_Half needs service”);
#endif
ci->di_bf = 0;
ci->di_which = 1; /* 2nd half of DMA buffer */
moveData = 1;
}
/*
* Move data if needed
*/
if ( moveData ) {
/* move data for Play if only data available */
if ( playing ) {
/* No more data..end of play */
if ( ci->ri_full <= 0 ) {
if (ci->di_state & DI_DMA_END_PLAY ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,”rapintr: End of Play Reached”);
#endif
if ( ci->ri_state & RI_WANTED_EMPTY ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: Cir.Buff is Wanted Empty”);
#endif
ci->ri_state &= ~RI_WANTED_EMPTY;
wakeup (ci);
}
else rapStop(DI_DMA_PLAYING);
return;
} else {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: Playing but no Full buffers”);
#endif
return;
}
}
/* Data is available to play */
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: Playing..which = %d, idx = %d, full = %d, Empty = %d”,
ci->di_which, ci->di_idx, ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free);
#endif
rapBufToDma(DMA_HALF_SIZE);
} /* if playing */
else { /* recording */
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: Recording..which = %d, full = %d, Empty = %d”,
ci->di_which, ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free);
#endif
rapDmaToBuf(DMA_HALF_SIZE);
}
} /* if move data */
else { /* no need to move data */
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapintr: Waiting for next interrupt, bf = %d, bh = %d”,
ci->di_bf, ci->di_bh);
#endif
}
gpis = INPW(addr+GPIS);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapintr: next Gpis = %x”, gpis);
#endif
} /* while ( gpis & .. */
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapintr: finished ...”);
#endif
} /*** End rapintr ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p i o c t l
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapioctl
* Purpose: handles IOCTL calls for RAP-10.
* Returns: 0 = Success, or errno
*************************************************************************/
int
rapioctl (dev_t dev, int cmd, void *arg, int mode, cred_t *cred, int *ret)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
ci = &cardInfo;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapioctl: Cmd = %d, full = %d, Empty = %d”,
cmd, ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free );
#endif
/*
* No card is installed or card is already opened
*/
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_INSTALLED) )
return (ENODEV);
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_OPENED) )
return (EACCES);
if ( ci->ci_pid != User_pid )
return (EACCES);
*ret = 0;
switch ( cmd ) {
case RAPIOCTL_END_PLAY:
/*=======================*
* End PLAY *
*=======================*/
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_PLAYING) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapioctl: End_PLay command in wrong state”);
#endif
return (EACCES);
}
return (rapClose (0) );
case RAPIOCTL_END_RECORD:
/*=======================*
* End RECORD *
*=======================*/
if ( !(ci->ci_state & CARD_RECORDING) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapioctl: End_Recrd command in wrong state”);
#endif
return (EACCES);
}
return (rapClose (0) );
} /* switch */
return (0);
} /** End rapioctl **/
/****************************************************************************
****** I n t e r n a l R o u t i n e s *******
****************************************************************************/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p C l o s e
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapClose
* Purpose: Routine to actually ends current operation and releases
* the card. It is written as a separate routine here so
* it can be shared by rapclose() and rapioctl() routines.
* One frees up the card, one does not. Also if we are called
* from ioctl, we will wait till all buffers are played (if
* in Playback mode).
* Returns: 0 = Success, or errno
*************************************************************************/
int
rapClose( uchar_t relCard )
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
rwBuf_t *rw;
int s, totLeft;
ci = &cardInfo;
s = LOCK();
rw = &rwQue[ci->ri_idx];
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapClose: relCard = %d, ci_state = %x, di_state = %x”,
relCard, ci->ci_state, ci->di_state );
#endif
/*
* if we are not recording and are not playing
* then simply mark the card as not opened and return
*/
if ( !(ci->ci_state & (CARD_RECORDING | CARD_PLAYING)) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapClose: Idle card ..closing”);
#endif
if ( relCard ) {
ci->ci_state &= ~CARD_OPENED;
ci->ci_pid = 0;
}
UNLOCK(s);
return(0);
}
/*
* Recording ? end it.
*/
if ( ci->ci_state & CARD_RECORDING ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,”rapClose: Ending Record (A/D)”);
#endif
rapStop(DI_DMA_RECORDING);
if ( relCard ) {
ci->ci_state &= ~CARD_OPENED;
ci->ci_pid = 0;
}
UNLOCK(s);
return(0);
}
/*
* playback and called from close() routine ?
* End the playback
*/
if ( relCard ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapClose: Ending Playback (D/A”);
#endif
rapStop(DI_DMA_PLAYING);
ci->ci_state &= ~CARD_OPENED;
ci->ci_pid = 0;
UNLOCK(s);
return(0);
}
/*
* Called from Ioctl.
* Closing in middle of play is different based on we
* have been called from close() routine or not.
* If called from Ioctl (relCard = 0), we will wait till
* all buffers are played back.
*/
if ( !(rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) && (rw->rw_count > 0) ) {
totLeft = RW_BUF_SIZE - rw->rw_count;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapClose: Current Buf %d has %d data. Filled with %d zeros”,
rw->rw_idx, rw->rw_count, totLeft );
#endif
if ( totLeft > 0 ) {
bzero (ci->ri_ptr, totLeft);
ci->ri_ptr += totLeft;
}
rapMarkBuf(rw, ci, RW_FULL);
}
/* some buffers to play */
if ( ci->ri_full > 0 ) {
/* Playback has not started yet */
if ( ci->di_state == DI_DMA_IDLE ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapClose: Starting playback, full = %d, empty = %d”,
ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free);
#endif
rapStart(DI_DMA_PLAYING);
}
ci->di_state = DI_DMA_IDLE;
ci->di_state |= DI_DMA_END_PLAY;
/* wait till buffers are all played back */
while ( ci->ri_full > 0 ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapClose: waiting for Play to end..full = %d, empty = %d, ri_idx = %d, di_idx = %d”,
ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free, ci->ri_idx, ci->di_idx);
#endif
ci->ri_state |= RI_WANTED_EMPTY;
if ( sleep (ci, PUSER | PCATCH) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapClose: Interrupted”);
#endif
rapStop(DI_DMA_PLAYING);
ci->ci_state &= ~CARD_OPENED;
ci->ci_pid = 0;
UNLOCK(s);
return (EINTR);
}
}
rapStop(DI_DMA_PLAYING);
}
else {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapClose: Circular buffer empty..closing”);
#endif
rapStop(DI_DMA_PLAYING);
}
UNLOCK(s);
return(0);
} /*** End rapClose ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p S t o p
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapStop
* Purpose: Stops D/A and A/D conversion.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapStop( uchar_t what )
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
rwBuf_t *rw;
caddr_t addr;
uchar_t dacm, adcm;
ushort_t gpdi;
int s, i;
s = LOCK();
ci = &cardInfo;
addr = ci->ci_addr[0];
gpdi = adcm = dacm = 0;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapStop: Stoping %s, full = %d, Empty = %d”,
(what == DI_DMA_PLAYING ? “Playback(D/A)”:”Record(A/D)”),
ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free);
#endif
switch ( what ) {
/* stop D/A Conversion (Playing) */
case DI_DMA_PLAYING:
ci->di_which = 0;
rapZeroDma(ci, DMA_BUF_SIZE);
OUTB(addr+DACM, dacm);
rapNoteOff (ci);
break;
/* stop A/D Conversion (recording) */
case DI_DMA_RECORDING:
OUTB(addr+ADCM, adcm);
OUTB(addr+DACM, dacm);
break;
}
OUTW(addr+GPDI, gpdi);
rapReleaseDma(ci);
/* Initialize Card Info structure */
ci->ci_state &= ~(CARD_PLAYING | CARD_RECORDING);
ci->ri_idx = 0;
ci->di_idx = 0;
ci->ri_state = 0;
ci->di_state = 0;
ci->di_ptr = rwQue[0].rw_buf;
ci->ri_ptr = rwQue[0].rw_buf;
ci->ri_free = RW_BUF_COUNT;
ci->ri_full = 0;
/* Initialize Circular Buffers */
for ( i = 0; i < RW_BUF_COUNT; i++ ) {
rw = &rwQue[i];
rw->rw_count = 0;
rw->rw_state = 0;
rw->rw_idx = i;
bzero (rw->rw_buf, RW_BUF_SIZE);
}
/* clear out any hanging GPIS and DACM */
gpdi = INPW(addr+GPIS);
UNLOCK(s);
} /** End rapStop **/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p S t a r t
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapStart
* Purpose: Prepares Eisa DMA buffers/Control block for Playing/Recording
* This function is called when DMA is Idle.
* Returns: 0 = Success or Error number.
*************************************************************************/
static int
rapStart (uchar_t what)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
dmaBuf_t *dmaB;
dmaCb_t *dmaC;
uchar_t stereo;
int err;
ci = &cardInfo;
stereo = (ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapStart: Starting %s, full = %d, empty = %d”,
(what == DI_DMA_PLAYING ? “Playback(D/A)”:”Record(A/D)”),
ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free );
#endif
/* clear Dma buffers */
ci->di_which = 0;
rapZeroDma(ci, DMA_BUF_SIZE);
/* check for Dma buffer addresses */
if ( (ci->ci_dmaBuf5 == (dmaBuf_t *)0) ||
(ci->ci_dmaCb5 == (dmaCb_t *)0) ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapStart: Chan 5 dmaBuf/dmaCb is NULL, what = %d”, what);
return(EIO);
}
if ( (ci->ci_dmaBuf6 == (dmaBuf_t *)0) ||
(ci->ci_dmaCb6 == (dmaCb_t *)0) ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapStart: Chan 6 dmaBuf/dmaCb is NULL, what = %d”, what);
return(EIO);
}
/*
* Prepare Eisa Buf and Cb for Channel 5. If in
* stereo mode, do the same for Channel 6.
*/
dmaB = ci->ci_dmaBuf5;
dmaC = ci->ci_dmaCb5;
rapPrepEisa (dmaB, dmaC, what, dmaLeftPhys );
if ( stereo ) {
dmaB = ci->ci_dmaBuf6;
dmaC = ci->ci_dmaCb6;
rapPrepEisa (dmaB, dmaC, what, dmaRightPhys );
}
/*
* Program Eisa DMA Channels
*/
err = eisa_dma_prog (ci->ci_adap, ci->ci_dmaCb5, ci->ci_dmaCh5,
EISA_DMA_NOSLEEP);
if ( err == 0 ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN, “rapStart: DMA Channel %d is busy”,
ci->ci_dmaCh5 );
return (EBUSY);
}
if ( stereo ) {
err = eisa_dma_prog (ci->ci_adap, ci->ci_dmaCb6, ci->ci_dmaCh6,
EISA_DMA_NOSLEEP);
if ( err == 0 ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapStart: DMA Channel %d is busy”,
ci->ci_dmaCh6 );
return (EBUSY);
}
}
/* enable hardware recognition on Eisa Dma Channels */
eisa_dma_enable (ci->ci_adap, ci->ci_dmaCb5, ci->ci_dmaCh5,
EISA_DMA_NOSLEEP);
if ( stereo ) {
eisa_dma_enable (ci->ci_adap, ci->ci_dmaCb6, ci->ci_dmaCh6,
EISA_DMA_NOSLEEP);
}
/* set Eisa DMA register for Autoinit mode */
rapSetAutoInit(ci, what);
ci->di_state |= what;
/* let's do it ! */
if ( what == DI_DMA_PLAYING ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapStart: Starting DMA for D/A Play”);
#endif
rapStartDA();
}
else {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapStart: Starting DMA for A/D Record”);
#endif
rapStartAD();
}
return(0);
} /** End rapStart **/
/************************************************************************
* r a p P r e p E i s a
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapPrepEisa
* Purpose: prepares EISA Buf and Cb structures.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapPrepEisa( dmaBuf_t *dmaB, dmaCb_t *dmaC, uchar_t what, paddr_t addr)
{
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapPrepEisa: Preparing Eisa DMA buffers for %s”,
(what == DI_DMA_PLAYING ? “Playback(D/A)” : “Record(A/D)” ) );
#endif
/* prepare Eisa DMA Buf struct */
bzero (dmaB, sizeof(dmaBuf_t) );
dmaB->count = DMA_BUF_SIZE;
dmaB->address = addr;
/* prepare Eisa DMA Control Block */
bzero (dmaC, sizeof(dmaCb_t) );
dmaC->reqrbufs = dmaB;
dmaC->reqr_path = EISA_DMA_PATH_16;
dmaC->trans_type = EISA_DMA_TRANS_DMND;
dmaC->targ_step = EISA_DMA_STEP_INC;
dmaC->bufprocess = EISA_DMA_BUF_SNGL;
if ( what == DI_DMA_PLAYING )
dmaC->cb_cmd = EISA_DMA_CMD_READ; /* mem -> rap10 */
else
dmaC->cb_cmd = EISA_DMA_CMD_WRITE; /* rap10 -> mem */
} /*** End rapPrepEisa ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p S t a r t D A
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapStartDA
* Purpose: Enables appropriate RAP interrupts and starts D/A Dma.
* Returns: None
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapStartDA()
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
caddr_t addr;
ushort_t gpdi, gpis, gpst, dtcd, mask;
uchar_t gpcm, pwmd, adcm, dacm;
uchar_t stereo;
int s;
ci = &cardInfo;
addr = ci->ci_addr[0];
stereo = ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapStartDA: Starting D/A Dma, full = %d, empty = %d”,
ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free );
#endif
/*
* Prepare the board for Record (A/D)
* Here is what we will do (in exact order):
*
* GPDI: Stereo = 0xA800, Mono = 0x9800
* itc = 1, dma transfer match count
* Stereo: Drq1->Dma5, Drq0->Dma6
* Mono: Drq1->Dma5
* Dt1, Dt0 = 10, Chan 1 ->Drq1, Chan 0 ->Drq0
* Left Chan->Drq1, Right Chan->Drq0
*
* DACM: Stereo: BF, Mono: BE
* scc = 1, Dma size in byte
* ts1 = ts2 = 1, transfer size of 4096 bytes
* dl1 = dl0 = 1; Data length of 16 bits for both Channels.
* Stereo ? ds1 = ds0 = 1 Start D/A on both Channels.
* Mono ? ds1 = 1 Start D/A on Channel 1
*
* GPCM: Select Mike level = 0x04
* Aux level = 0x08
* PWMD: 0xFF (Max level)
*/
gpdi = (stereo ? 0xA800: 0x9800);
dacm = (stereo ? 0xBF:0xBE);
gpcm = 0x04;
pwmd = 0xFF;
mask = (stereo ? (GPIS_DN1|GPIS_DN0): GPIS_DN1);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapStartDA: gpdi = %x, dacm = %x”, gpdi, dacm);
#endif
/* Set Rap-10 card */
OUTB(addr+GPCM, gpcm);
OUTB(addr+PWMD, pwmd);
OUTW(addr+GPDI, gpdi);
OUTB(addr+DACM, dacm);
/*
* Busy-wait for both Note_On interrupts
* The interrupt version is commenetd out for now.
*/
gpis = INPW(addr+GPIS);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapStartDA: Waiting for Note_On, gpis = %x, mask = %x”,
gpis, mask);
#endif
while ( !(gpis & mask) ) {
gpis = INPW(addr+GPIS);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapStartDA: Waiting ..new gpis = %x”, gpis);
#endif
}
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapStartDA: Note_On Interrupt Received, gpis = %x”,
gpis );
#endif
rapNoteOn(ci, gpis);
} /*** End rapStartDA ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p S t a r t A D
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapStartAD
* Purpose: Enables appropriate RAP interrupts and starts A/D Dma.
* Returns: None
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapStartAD()
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
caddr_t addr;
ushort_t gpdi;
uchar_t gpcm, pwmd, adcm, dacm;
uchar_t stereo, mic;
ci = &cardInfo;
addr = ci->ci_addr[0];
stereo = ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapStartAD: Starting A/D Dma in %s, full = %d, empty = %d”,
(stereo ? “Stereo”:”Mono”), ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free );
#endif
/*
* Prepare the board for Record (A/D)
* Here is what we will do (in exact order):
*
* GPDI: Stereo = 0xA400, Mono = 0x9400
* itc = 1, dma transfer match count
* Stereo: Drq1->Dma5, Drq0->Dma6
* Mono: Drq1->Dma5
* Dt1, Dt0 = 01, Left Chan->Drq1, Right Chan->Drq0
*
* DACM: 0xB0
* scc = 1, Dma size in byte
* ts1 = ts2 = 1, transfer size of 4096 bytes
*
* GPCM: Select Mic level = 0x04
* Aux level = 0x08
* PWMD: 0xFF (Max level)
*
* ADCM: Stereo: Mic 0x6F, line 0x4F,
* Mono: Mic 0x6D, line 0x4D
* Mon = 1, Monitor ON
* Gin = 1, Head Amp Gain to Mic.
* Af1, Af0 = 01, 22.05 KHz
* Adl = 1, 16 bit data length
* Stereo, Adm = 1, else = 0
* Ads = 1, Start A/D
*/
gpdi = (stereo ? 0xA400: 0x9400);
gpcm = 0x08;
adcm = (stereo ? 0x6F:0x6D);
dacm = 0xB0;
gpcm = 0x04;
pwmd = 0xFF;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapStartAD: Rap init as: gpdi = %x, dacm = %x, gpcm = %x, adcm = %x”,
gpdi, dacm, gpcm, adcm);
#endif
OUTW(addr+GPDI, gpdi);
OUTB(addr+DACM, dacm);
OUTB(addr+GPCM, gpcm);
OUTB(addr+PWMD, pwmd);
OUTB(addr+ADCM, adcm);
} /*** End rapStartAD ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p B u f T o D m a
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapBufToDma
* Purpose: moves data from current rwQue[] entry to DMA buffers.
* This routine is called by INterrupt handler only except
* once before we startd D/A (when no DMA is programmed yet)
* Returns: None
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapBufToDma( int bytes)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
rwBuf_t *rw;
uchar_t *dmaR;
uchar_t *dmaL;
uchar_t stereo;
int i, j, s;
ci = &cardInfo;
rw = &rwQue[ci->di_idx];
stereo = ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO;
/*
* filling 1st half or 2nd half of the buffers ?
*/
if ( ci->di_which ) {
dmaR = &dmaRight[DMA_HALF_SIZE];
dmaL = &dmaLeft[DMA_HALF_SIZE];
if ( bytes == DMA_BUF_SIZE ) {
bytes = DMA_HALF_SIZE;
}
}
/* filling 1st half of dma buffers */
else {
dmaR = &dmaRight[0];
dmaL = &dmaLeft[0];
}
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapBufToDma: Bytes = %d, which = %d, Idx = %d, rw_count = %d, Full = %d, Empty = %d”,
bytes, ci->di_which, ci->di_idx, rw->rw_count, ci->ri_full,
ci->ri_free);
#endif
/*
* if buffer is not Full, we zero out dma buffers and
* return. We cannot wait till it gets Full.
*/
if ( !(rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) ) {
rapZeroDma(ci, bytes);
ci->di_ptr = NULL;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapBufToDma: Buf %d is not Full, rw_state = %x”,
rw->rw_idx, rw->rw_state );
#endif
return;
}
/* buffer is full of data ..readjust the buffer pointer */
if ( ci->di_ptr == NULL )
ci->di_ptr = rw->rw_buf;
/*
* Fill buffers ...
*/
for ( i = 0; i < bytes; i++ ) {
/*
* First check if buffer is empty. If it is, mark it
* as empty, wake anyone up who wants it and get the
* next full buffer.
*/
if ( rw->rw_count <= 0 ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapBufToDma: Buf %d is Empty now, rw_count = %d”,
rw->rw_idx, rw->rw_count );
#endif
rapMarkBuf(rw, ci, RW_EMPTY);
ci->di_ptr = NULL;
if ( rw->rw_state & RW_WANTED_EMPTY ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapBufToDma: Buf %d is Wanted_Empty”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_EMPTY;
wakeup(rw);
}
j = rapGetNextFull (ci->di_idx, FROM_INTR);
if ( j == -1 ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapBufToDma: Could not get next Full buffer”);
#endif
break;
}
ci->di_idx = j;
rw = &rwQue[ci->di_idx];
ci->di_ptr = rw->rw_buf;
continue;
}
/* buffer still has some data ..move them */
if ( stereo ) {
dmaL[i] = *(ci->di_ptr++);
dmaR[i] = *(ci->di_ptr++);
rw->rw_count -= 2;
}
else {
dmaL[i] = *(ci->di_ptr++);
rw->rw_count--;
}
} /* for .. */
/* Flush the cache line so that Dma buffers contain all data */
dki_dcache_wbinval (dmaL, (unsigned)bytes);
if ( stereo )
dki_dcache_wbinval (dmaR, (unsigned)bytes);
} /*** end rapBufToDma ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p D m a T o B u f
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapDmaToBuf
* Purpose: Moves data from DMA buffers (Right and Left in stereo)
* into a rwQue entry. This routine is called only by
* Interrupt Handler.
* Returns: None
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapDmaToBuf( int bytes)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
rwBuf_t *rw;
uchar_t *dmaR;
uchar_t *dmaL;
uchar_t stereo;
int i, j, s, inc;
ci = &cardInfo;
rw = &rwQue[ci->di_idx];
stereo = ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO;
/*
* filling 1st half or 2nd half of the buffers ?
*/
if ( ci->di_which ) {
dmaR = &dmaRight[DMA_HALF_SIZE];
dmaL = &dmaLeft[DMA_HALF_SIZE];
if ( bytes == DMA_BUF_SIZE ) {
bytes = DMA_HALF_SIZE;
}
}
/* filling 1st half of dma buffers */
else {
dmaR = &dmaRight[0];
dmaL = &dmaLeft[0];
}
/* Invalidate the Cache */
dki_dcache_inval (dmaL, (unsigned)bytes);
if ( stereo )
dki_dcache_inval (dmaR, (unsigned)bytes);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapDmaToBuf: Bytes= %d, Idx = %d, rw_count = %d, Full = %d, Empty= %d”,
bytes, ci->di_idx, rw->rw_count, ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free);
#endif
/*
* if buffer is Full ..we cannot wait ! Ignore new data
* by simply returning.
*/
if ( rw->rw_state & RW_FULL ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapDmaToBuf: Buf %d is not Empty ..Ignoring data”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
return;
}
/* buffer is Empty ..calculate the end address */
if ( ci->di_ptr == NULL )
ci->di_ptr = rw->rw_buf;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapDmaToBuf: Moving %s of DMA buffers in %s, rw_count = %x”,
(ci->di_which ? “Second Half” : “First Half”),
(stereo ? “Stereo”:”Monoe”), rw->rw_count);
#endif
/*
* Fill buffers ...in stereo bytes are Left:Right:Left:Right...
*/
for ( i = 0; i < bytes; i++ ) {
/*
* First check if this buffer is Full or not.
* If it is, mark it as Full and wake anyone up who is
* waiting for it. Then get the next Empty buffer.
*/
if ( rw->rw_count >= RW_BUF_SIZE ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapDmaToBuf: Buf %d is Full now, rw_count = %d”,
rw->rw_idx, rw->rw_count );
#endif
rapMarkBuf(rw, ci, RW_FULL);
if ( rw->rw_state & RW_WANTED_FULL ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapDmaToBuf: Buf %d is Wanted_Full”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_FULL;
wakeup(rw);
}
j = rapGetNextEmpty(ci->di_idx, FROM_INTR);
if ( j == -1 ) {
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapDmaToBuf: Could not get next empty”);
return;
}
ci->di_idx = j;
rw = &rwQue[ci->di_idx];
ci->di_ptr = rw->rw_buf;
continue;
}
/* buffer still has room ...move data */
if ( stereo ) {
*(ci->di_ptr++) = dmaL[i];
*(ci->di_ptr++) = dmaR[i];
rw->rw_count += 2;
}
else {
*(ci->di_ptr++) = dmaL[i];
rw->rw_count++;
}
} /* while bytes ... */
} /*** end rapDmaToBuf ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p G e t N e x t F u l l
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapGetNextFull
* Purpose: returns the index of next Full entry in rwQue[],
* starting from a given index. Sleeps if the entry
* is not Full.
* Returns: the index of the empty entry.
*************************************************************************/
static short
rapGetNextFull (short idx, uchar_t fromIntr)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
int s;
toid_t to_id;
rwBuf_t *rw;
ci = &cardInfo;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapGetNextFull: Getting Next Full Buffer..idx = %d, fromIntr: %d”,
idx, fromIntr );
#endif
/* go to beginning if at the end of the queu */
idx++;
if ( idx >= RW_BUF_COUNT )
idx = 0;
rw = &rwQue[idx];
/*
* if buffer is not available and we were called from Intrupt
* handler, simply ignore the request and return error
*/
s = LOCK();
if ( !(rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) && (fromIntr) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapGetNextFull: Buffer %d is not Full. ..Cannot Wait”,
rw->rw_idx);
#endif
UNLOCK(s);
return(-1);
}
/* wait for the buffer to become Full */
if ( !(rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) ) {
ci->ri_tout = 0;
to_id = itimeout (rapTimeOut, rw, RW_TIMEOUT, plbase, 0, 0, 0);
while ( !(rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) && !ci->ri_tout ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapGetNextFull: Waiting for Buf %d to become Full”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
rw->rw_state |= RW_WANTED_FULL;
if ( sleep(rw, PUSER | PCATCH) ) {
untimeout(to_id);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapGetNextFull: Interrupted”);
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_FULL;
UNLOCK(s);
return(-1);
}
}
untimeout (to_id);
if ( ci->ri_tout ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “raGetNextFull: Timed out”);
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_FULL;
UNLOCK(s);
return (-1);
}
} /* if !(rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) */
UNLOCK(s);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapGetNextFull: next Full Buffer is %d”, idx);
#endif
return(idx);
} /*** End rapGetNextFull ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p G e t N e x t E m p t y
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapGetNextEmpty
*
* Purpose: returns the index of next empty entry in rwQue[],
* starting from a given index. Sleeps if the entry
* is not empty.
* Returns: the index of the empty entry.
*************************************************************************/
static short
rapGetNextEmpty (short idx, uchar_t fromIntr)
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
int s;
toid_t to_id;
rwBuf_t *rw;
ci = &cardInfo;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapGetNextEmpty: Getting Next Empty Buffer..idx = %d, fromIntr: %d”,
idx, fromIntr );
#endif
/* go to beginning if at the end of the queu */
idx++;
if ( idx >= RW_BUF_COUNT )
idx = 0;
rw = &rwQue[idx];
s = LOCK();
/*
* if buffer is nit available and we were called from Intrupt
* handler, simply ignore the request and return error
*/
if ( (rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) && (fromIntr) ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapGetNextEmpty: Buffer %d is not Empty ..Cannot Wait”,
rw->rw_idx);
#endif
UNLOCK(s);
return(-1);
}
/* wait for the buffer to become Empty */
if ( rw->rw_state & RW_FULL ) {
ci->ri_tout = 0;
to_id = itimeout (rapTimeOut, rw, RW_TIMEOUT, plbase, 0, 0, 0);
while ( (rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) && !ci->ri_tout ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapGetNextEmpty: Waiting for Buf %d to become Empty”,
rw->rw_idx );
#endif
rw->rw_state |= RW_WANTED_EMPTY;
if ( sleep(rw, PUSER | PCATCH) ) {
untimeout(to_id);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapGetNextEmpty: Interrupted”);
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_EMPTY;
UNLOCK(s);
return(-1);
}
} /* while .. */
untimeout (to_id);
if ( ci->ri_tout ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “raGetNextEmpty: Timed out”);
#endif
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_WANTED_EMPTY;
UNLOCK(s);
return (-1);
}
} /* if (rw->rw_state & RW_FULL) */
UNLOCK(s);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapGetNextEmpty: next Empty Buffer is %d”, idx);
#endif
return(idx);
} /*** End rapGetNextEmpty ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p D i s I n t
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapDisInt
* Purpose: Disables RAP-10 interrupts.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapDisInt( cardInfo_t *ci)
{
caddr_t addr;
ushort_t s;
uchar_t c;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapDisInt: full = %d, empty = %d, di_state = %d”,
ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free, ci->di_state );
#endif
addr = ci->ci_addr[0];
/* disable all Interrupts */
s = 0;
OUTW(addr+GPDI, s);
OUTB(addr+DACM, 0x00);
OUTB(addr+ADCM, 0x00);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapDisInt: Rap is set”);
#endif
} /*** End rapDisInt ***/
/**************************************************************************
* r a p G e t D m a *
**************************************************************************
* Name: rapGetDma
* Purpose: allocates dma Buf and Cb structures
* Returns: 0 = Success, 1 = Error
**************************************************************************/
static int
rapGetDma ( dmaBuf_t **dmaB, dmaCb_t **dmaC, int ch )
{
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapGetDma: Getting Eisa Dma Buf and Cb for Channel %d”, ch);
#endif
*dmaB = eisa_dma_get_buf (EISA_DMA_SLEEP);
if ( *dmaB == NULL )
return (1);
*dmaC = eisa_dma_get_cb ( EISA_DMA_SLEEP );
if ( *dmaC == NULL )
return (1);
return (0);
} /*** End rapGetDma ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p M a r k B u f
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapMarkBuf
* Purpose: Marks a buffer (Empty, Busy, Full) and increments/decrements
* appropriate counters. Buffers status changed as:
* Empty -> Busy -> Full -> Empty -> Busy ..
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapMarkBuf (rwBuf_t *rw, cardInfo_t *ci, uchar_t m)
{
int s;
s = LOCK();
switch ( m ) {
case RW_EMPTY:
rw->rw_state &= ~RW_FULL;
if ( ci->ri_full )
ci->ri_full--;
ci->ri_free++;
rw->rw_count = 0;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapMarkBuf: Buf %d set EMPTY. Full = %d, Emp = %d”,
rw->rw_idx, ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free );
#endif
break;
case RW_FULL:
rw->rw_state |= RW_FULL;
ci->ri_full++;
if ( ci->ri_free )
ci->ri_free--;
rw->rw_count = RW_BUF_SIZE;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapMarkBuf: Buf %d set FULL. Full = %d, Emp = %d”,
rw->rw_idx, ci->ri_full, ci->ri_free );
#endif
break;
}
UNLOCK(s);
} /*** End rapMarkBuf ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p K e r n M e m
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapKernMem
* Purpose: Allocates/Disallocates Kernel memory for Right and
* Left DMA channels.
* Returns: 0 = Success, 1 = Failure.
*************************************************************************/
static int
rapKernMem ( uchar_t what)
{
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapKernMem: %s Kernel Contigious Memory”,
(what == 1 ? “Allocating” : “Deallocating”) );
#endif
switch ( what ) {
/*=======================================*
* Allocate Right/Left DMA Channels *
*=======================================*/
case 1:
dmaRight = kmem_alloc (DMA_BUF_SIZE,
KM_NOSLEEP | KM_PHYSCONTIG | KM_CACHEALIGN );
if ( dmaRight == (caddr_t)NULL ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapKernMem: Cannot allocate DMA memory for R_chann”);
return(1);
}
dmaLeft = kmem_alloc (DMA_BUF_SIZE,
KM_NOSLEEP | KM_PHYSCONTIG | KM_CACHEALIGN );
if ( dmaLeft == (caddr_t)NULL ) {
cmn_err (CE_WARN,
“rapKernMem: Cannot allocate DMA memory for L_chann”);
kmem_free (dmaRight, DMA_BUF_SIZE);
return(1);
}
/* get the physicall address */
dmaRightPhys = kvtophys(dmaRight);
dmaLeftPhys = kvtophys(dmaLeft);
return(0);
/*=======================================*
* Deallocate Right/Left DMA Channels *
*=======================================*/
case 2:
if ( dmaRight != NULL ) {
kmem_free (dmaRight, DMA_BUF_SIZE);
dmaRight = (caddr_t)NULL;
}
if ( dmaLeft != NULL ) {
kmem_free (dmaLeft, DMA_BUF_SIZE);
dmaLeft = (caddr_t)NULL;
}
return(0);
} /* switch */
} /*** End rapKernMem ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p T i m e O u t
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapTimeOut
* Purpose: is called when Read/Write waiting for buffers time out.
* Returns:
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapTimeOut( void *addr )
{
cardInfo_t *ci;
ci = &cardInfo;
/* indicate a timeout */
ci->ri_tout = 1;
wakeup (addr);
}
/*************************************************************************
* r a p N o t e O n
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapNoteOn
* Purpose: Sends a MIDI Note_On message.
* This code is taken from RAP-10 manual.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapNoteOn ( cardInfo_t *ci, ushort_t orig_gpis)
{
int s, stereo;
uchar_t c, pan, rank, chksum, sum;
caddr_t addr;
ushort_t gpis;
addr = ci->ci_addr[0];
stereo = ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO;
pan = 0x40;
rank = 0x01; /* for 22050 Hz */
gpis = orig_gpis;
/*
* Busy wait till Txd Fifo is empty
* The interrupt version is commenetd out below
*/
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapNoteOn: Waiting for Txd Fifo Empty, gpis = %x”,
gpis);
#endif
while ( !(gpis & GPIS_TXD) ) {
gpis = INPW(addr+GPIS);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapNoteOn: Waiting ..new gpis = %x”, gpis);
#endif
}
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapNoteOn: Issuing a Note_On SysEx Cmd”);
#endif
/* send Note_On */
c = 0xf0; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x41; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x10; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x56; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x12; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
if ( stereo ) {
c = 0x03; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x00; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x01; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
sum = 0x03 + 0x01;
}
else {
c = 0x02; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x00; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x0A+0x01; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
sum = 0x02+0x0A+0x01;
}
c = 0x01; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x7F; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x7F; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, rank);
sum += (0x01+0x7F+0x7F+rank);
c = 0x40; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x00; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
c = 0x40; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, pan);
sum += (0x40+0x40+pan);
/* calculate the checksum */
chksum = (0x80 - (sum % 0x80)) & 0x7F;
OUTB(addr+MDTD, chksum);
c = 0xF7; OUTB(addr+MDTD, c);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapNoteOn: Note_On Issued, chksum = %x”, chksum);
#endif
} /* end rapNoteOn */
/*************************************************************************
* r a p N o t e O f f
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapNoteOff
* Purpose: Sends a MIDI Note_Off message.
* This code is taken from RAP-10 manual.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapNoteOff ( cardInfo_t *ci)
{
int s, stereo;
uchar_t pan, b, rank, sum, chksum;
caddr_t addr;
ushort_t gpis;
addr = ci->ci_addr[0];
stereo = ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO;
pan = 0x40;
rank = 0x01; /* for 22050 Hz */
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapNoteOff: Waiting for Txd Empty”);
#endif
/* wait till Txd is Empty */
gpis = INPW(addr+GPIS);
while ( !(gpis & GPIS_TXD) ) {
us_delay(10);
gpis = INPW(addr+GPIS);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapNoteOff: Waiting ..new gpis = %x”, gpis);
#endif
}
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapNoteOff: Issuing Note_Off”);
#endif
/* send Note_On */
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0xF0);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x41);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x10);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x56);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x12);
if ( stereo ) {
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x03);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x00);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x01);
sum = 0x03 + 0x01;
}
else {
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x02);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x00);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x0A+0x01);
sum = 0x02 + 0x0A + 0x01;
}
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x00);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x7F);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x7F);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x00);
sum += 0x7F + 0x7F;
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x40);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x00);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x40);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, pan);
sum += 0x40 + 0x40 + pan;
/* calculate checksum */
chksum = (0x80 - (sum % 0x80)) & 0x7F;
OUTB(addr+MDTD, chksum);
OUTB(addr+MDTD, 0x7F);
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapNoteOff: Note_On Issued, chksum = %x”, chksum);
#endif
} /* end rapNoteOff */
/*************************************************************************
* r a p Z e r o D m a
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapZeroDma
* Purpose: Zero outs DMA buffers.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapZeroDma (cardInfo_t *ci, int bytes)
{
caddr_t dmaL, dmaR;
int stereo, s;
s = LOCK();
stereo = ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO;
/*
* Zero out which half ?
*/
if ( ci->di_which ) {
dmaR = &dmaRight[DMA_HALF_SIZE];
dmaL = &dmaLeft[DMA_HALF_SIZE];
if ( bytes == DMA_BUF_SIZE ) {
bytes = DMA_HALF_SIZE;
}
}
/* Zer out 1st half of dma buffers */
else {
dmaR = &dmaRight[0];
dmaL = &dmaLeft[0];
}
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapZeroDma: Zeroing out %s of Dma buffers in %s for %d bytes”,
(ci->di_which ? “2nd half”:”1st half”),
(stereo ? “Stereo”:”Mono”),
bytes);
#endif
bzero (dmaL, bytes);
dki_dcache_wbinval (dmaL, (unsigned)bytes);
if ( stereo ) {
bzero (dmaR, bytes);
dki_dcache_wbinval (dmaR, (unsigned)bytes);
}
UNLOCK(s);
} /*** end rapZeroDma ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p R e l e a s e D m a
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapReleaseDma
* Purpose: Releases Dma channel(s).
* Note that we access kernel's Dma structure and later on
* a routine will be provided for us to avoid this.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
static void
rapReleaseDma (cardInfo_t *ci)
{
/* disable Eisa Dma */
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapReleaseDma: Releasing Eisa Dma Chann %d”,
ci->ci_dmaCh5);
#endif
eisa_dma_disable(0, ci->ci_dmaCh5);
if ( ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO ) {
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE, “rapReleaseDma: Releasing Eisa Dma Chann %d”,
ci->ci_dmaCh6);
#endif
eisa_dma_disable(0, ci->ci_dmaCh6);
}
} /*** end rapReleaseDma ***/
/*************************************************************************
* r a p S e t A u t o I n i t
*************************************************************************
* Name: rapSetAutoInit
* Purpose: sets Eisa DMA register for Autoinit. In Autoinit, DMA
* starts over from the beginning of the buffer again once it
* has transfered all bytes in the buffer.
* Returns: None.
*************************************************************************/
#define EISA_MODE_REG 0xd6
#define EISA_CH5 0x01
#define EISA_CH6 0x02
#define EISA_WRITE 0x04
#define EISA_READ 0x08
#define EISA_AUTO 0x10
static void
rapSetAutoInit( cardInfo_t *ci, uchar_t what)
{
uchar_t b;
#ifdef DEBUG
cmn_err (CE_NOTE,
“rapSetAutoInit: setting Autoinit DMA for %s, Eisa Addr = %x”,
( what == DI_DMA_PLAYING ? “Playback(D/A)” : “Record(A/D)” ),
eisa_addr );
#endif
b = 0;
if ( what == DI_DMA_PLAYING )
b |= EISA_READ; /* Memory -> Device */
else
b |= EISA_WRITE; /* Device -> Memory */
/* Autoinit for Channel 5 - Demand Mode select is default */
b |= (EISA_AUTO | EISA_CH5);
OUTB(eisa_addr+EISA_MODE_REG, b);
/* Autoinit for Channel 6 (if in stereo mode) */
if ( ci->ci_state & CARD_STEREO ) {
b &= ~EISA_CH5;
b |= EISA_CH6;
OUTB(eisa_addr+EISA_MODE_REG, b);
}
} /*** End rapSetAutoInit ***/
|