This chapter provides software guidelines to operate the Vault and
SCSIBox 2. This upgrade requires IRIX 5.0 or later.
Disk striping increases workstation throughput by distributing file data across multiple disk drives through logical volumes. For detailed software descriptions of how hard drives are configured to support disk striping, see the “Logical Volumes” subsection in the IRIX Advanced Site and Server Administration Guide.
| Caution: Systems utilizing disk striping must have a well-tested and maintained backup plan. If a single disk drive failure occurs, the entire file structure can be affected because sections of the filesystem are distributed among different disk drives. |
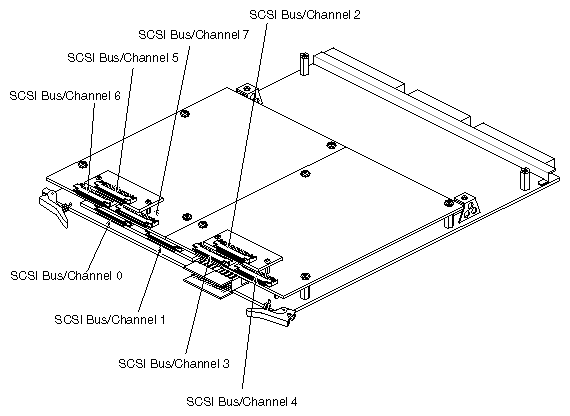
An IO4 board can have up to eight SCSI bus interfaces (or channels). See Figure B-1. Compare this with the IO3, the predecessor to the IO4, which has only two channels (or SCSI bus interfaces). In addition, the new, wider 68-pin SCSI connector on the chassis now enables connectivity with up to 15 devices per channel.
Due to this expanded connectivity, the IRIX and PROM monitor drive addressing scheme has been modified to accommodate the increased number of drives and channels.
The previous PROM drive addressing format remains in place; for example:
dksc(a,b,c)
where a represents the SCSI bus number, b refers to the drive number, and c refers to the drive's partition number. The dksc designation is the monitor's name for SCSI.
| Note: The PROM can address only the master IO4 board in a system. In a deskside system, the master IO4 resides in either slot 3 (Onyx) or slot 5 (CHALLENGE). In a rackmount system, the master IO4 resides in slot 15. If you need to address a drive connected to another IO4 board, you must do so under IRIX. |
Under IRIX, the addressing scheme has changed as shown in the following new format:
/dev/dsk/dksSSSdDsP
where /dev/dsk references the IRIX file directory of the drives and dks designates SCSI. The SSS designator represents the slot number of the IO4 board and/or the SCSI bus number (see Note below), dD refers to the drive number, and sP refers to the drive's partition number.
| Note: If you are addressing a drive on the master IO4 board system, you need to specify only the applicable SCSI bus number. If you are addressing a drive on another IO4 board, you must specify both the slot number of the board and the applicable SCSI bus number. |
If, for example, you are addressing a drive connected to an IO4 board in slot 4 and SCSI bus number 5 (on a deskside system), the SSS number would be 45.
With the earlier IO3 boards, the software required only single digits to differentiate drives; however, with the IO4 and new version of the software, the SCSI bus or SSS number can contain up to three digits. If SSS is a two- or three-digit number, the first one or two digits identify the IO4 board by the Ebus slot number. The final digit identifies which of the eight possible SCSI buses (0 through 7) on the IO4 board is used. Figure B-1 illustrates how the buses are physically laid out on the IO4 board.
The software drive identification number uses the same form as in the addressing scheme described earlier. Insert the IO4 board slot number and/or the SCSI bus number, followed by the drive number and partition number, as required.
Assume that you want to address partition 0 on SCSI drive number 6. This drive connects to SCSI bus number 6. You can also assume that the master IO4 resides in slot number 15 in a rackmount system.
The PROM drive address is:
dksc(6,6,0)
Assume that you want to address partition 0 on SCSI drive (number 6). This drive connects to SCSI bus number 6. Also assume that the IO4 resides in slot number 14.
The IRIX drive address is:
/dev/dsk/dks146d6s0