This chapter provides an introduction to Performance Co-Pilot (PCP), an overview of its individual components, and conceptual information to help you use this product.
The following sections are included:
“Objectives” covers the intended purposes of PCP.
“Overview of Component Software”, describes PCP tools and agents.
“Conceptual Foundations”, discusses the design theories behind PCP.
“Product Extensibility”, discusses the extensibility of the PCP product.
Performance Co-Pilot (PCP) provides a range of services that may be used to monitor and manage system performance. These services are distributed and scalable to accommodate the most complex system configurations and performance problems.
PCP is targeted at the performance analyst, benchmarker, capacity planner, developer, database administrator, or system administrator with an interest in overall system performance and a need to quickly isolate and understand performance behavior, resource utilization, activity levels, and bottlenecks in complex systems. Platforms that can benefit from this level of performance analysis include large servers, server clusters, or multiserver sites delivering Database Management Systems (DBMS), compute, Web, file, or video services.
To deal efficiently with the dynamic behavior of complex systems, performance analysts need to filter out noise from the overwhelming stream of performance data, and focus on exceptional scenarios. Visualization of current and historical performance data, and automated reasoning about performance data, effectively provide this filtering.
From the PCP end user's perspective, PCP presents an integrated suite of tools, user interfaces, and services that support real-time and retrospective performance analysis, with a bias towards eliminating mundane information and focusing attention on the exceptional and extraordinary performance behaviors. When this is done, the user can concentrate on in-depth analysis or target management procedures for those critical system performance problems.
At the lowest level, performance metrics are collected and managed in autonomous performance domains such as the IRIX operating system, a DBMS, a layered service, or an end-user application. These domains feature a multitude of access control policies, access methods, data semantics, and multiversion support. All this detail is irrelevant to the developer or user of a performance monitoring tool, and is hidden by the PCP infrastructure.
Performance Metrics Domain Agents (PMDAs) within PCP encapsulate the knowledge about, and export performance information from, autonomous performance domains.
Usability and extensibility of performance management tools mandate a single scheme for naming performance metrics. The set of defined names constitutes a Performance Metrics Name Space (PMNS). Within PCP, the PMNS is adaptive so it can be extended, reshaped, and pruned to meet the needs of particular applications and users.
PCP provides a single interface to name and retrieve values for all performance metrics, independently of their source or location.
From a purely pragmatic viewpoint, a single workstation must be able to monitor the concurrent performance of multiple remote hosts. At the same time, a single host may be subject to monitoring from multiple remote workstations.
These requirements suggest a classic client-server architecture, which is exactly what PCP uses to provide concurrent and multiconnected access to performance metrics, independent of their host location.
Complex systems are subject to continual changes as network connections fail and are reestablished; nodes are taken out of service and rebooted; hardware is added and removed; and software is upgraded, installed, or removed. Often these changes are asynchronous and remote (perhaps in another geographic region or domain of administrative control).
The distributed nature of the PCP (and the modular fashion in which performance metrics domains can be installed, upgraded, and configured on different hosts) enables PCP to adapt concurrently to changes in the monitored system(s). Variations in the available performance metrics as a consequence of configuration changes are handled automatically and become visible to all clients as soon as the reconfigured host is rebooted or the responsible agent is restarted.
PCP also detects loss of client-server connections, and most clients support subsequent automated reconnection.
A range of tools is provided to support flexible, adaptive logging of performance metrics for archive, playback, remote diagnosis, and capacity planning. PCP archive logs may be accumulated either at the host being monitored, at a monitoring workstation, or both.
A universal replay mechanism, modeled on VCR controls, supports play, step, rewind, fast forward at variable speed processing of archived performance data.
Most PCP applications are able to process archive logs and real-time performance data with equal facility. Unification of real-time access and access to the archive logs, in conjunction with VCR-like viewing controls, provides new and powerful ways to build performance tools and to review both current and historical performance data.
For operational and production environments, PCP provides a framework with scripts to customize in order to automate the execution of ongoing tasks such as these:
Flexible alarm monitoring: parameterized rules to address common critical performance scenarios and facilities to customize and refine this monitoring
Retrospective performance audits covering the recent past; for example, daily or weekly checks for performance regressions or quality of service problems
PCP permits the integration of new performance metrics into the PMNS, the collection infrastructure, and the logging framework. The guiding principle is, “if it is important for monitoring system performance, and you can measure it, you can easily integrate it into the PCP framework.”
For many PCP customers, the most important performance metrics are not those already supported, but new performance metrics that characterize the essence of good or bad performance at their site, or within their particular application environment.
One example is an application that measures the round-trip time for a benign “probe” transaction against some mission-critical application.
For application developers, a library is provided to support easy-to-use insertion of trace and monitoring points within an application, and the automatic export of resultant performance data into the PCP framework. Other libraries and tools aid the development of customized and fully featured Performance Metrics Domain Agents (PMDAs).
Extensive source code examples are provided in the distribution, and by using the PCP toolkit and interfaces, these customized measures of performance or quality of service can be easily and seamlessly integrated into the PCP framework.
The core PCP modules support export of performance metrics that include all 6.5.x kernel instrumentation, hardware instrumentation, process-level resource utilization, and activity in the PCP collection infrastructure.
The supplied agents support over 1000 distinct performance metrics, many of which can have multiple values, for example, per disk, per CPU, or per process.
Performance Co-Pilot (PCP) is composed of text-based tools, optional graphical tools, and related commands. Each tool or command is fully documented by a man page. These man pages are named after the tools or commands they describe, and are accessible through the man command. For example, to see the pminfo(1) man page for the pminfo command, enter this command:
man pminfo |
Many PCP tools and commands are accessible from an Icon Catalog on the IRIX desktop, grouped under PerfTools. In the Toolchest Find menu, choose PerfTools; an Icon Catalog appears, containing clickable PCP programs. To bring up a Web-based introduction to Performance Co-Pilot, click the AboutPCP icon.
A list of PCP tools and commands, grouped by functionality, is provided in the following sections.
The following tools provide the principal services for the PCP end-user with an interest in monitoring, visualizing, or processing performance information collected either in real time or from PCP archive logs:
PCP provides the following tools to support real-time data collection, network transport, and archive log creation services for performance data:
PCP provides the following tools to support the PCP infrastructure and assist operational procedures for PCP deployment in a production environment:
The following sections provide a detailed overview of concepts that underpin Performance Co-Pilot (PCP).
Across all of the supported performance metric domains, there are a large number of performance metrics. Each metric has its own structure and semantics. PCP presents a uniform interface to these metrics, independent of the underlying metric data source.
The Performance Metrics Name Space (PMNS) provides a hierarchical classification of external metric names, and a mapping from external names to internal metric identifiers. See “Performance Metrics Name Space”, for a description of the PMNS.
When performance metric values are returned to a requesting application, there may be more than one value instance for a particular metric; for example, independent counts for each CPU, process, disk, or local filesystem. Internal instance identifiers correspond one to one with external (textual) descriptions of the members of an instance domain.
Transient performance metrics (such as per-process information, per-XLV volume, and so on) cause repeated requests for the same metric to return different numbers of values, or changes in the particular instance identifiers returned. These changes are expected and fully supported by the PCP infrastructure; however, metric instantiation is guaranteed to be valid only at the time of collection.
When performance metrics are retrieved, they are delivered in the context of a particular source of metrics, a point in time, and a profile of desired instances. This means that the application making the request has already negotiated to establish the context in which the request should be executed.
A metric source may be the current performance data from a particular host (a live or real-time source), or an archive log of performance data collected by pmlogger at some distant host or at an earlier time (a retrospective or archive source).
By default, the collection time for a performance metric is the current time of day for real-time sources, or current point within an archive source. For archives, the collection time may be reset to an arbitrary time within the bounds of the archive log.
| Note: Performance Co-Pilot 2.x, and IRIX release 6.5, were developed to be completely Year 2000 compliant. |
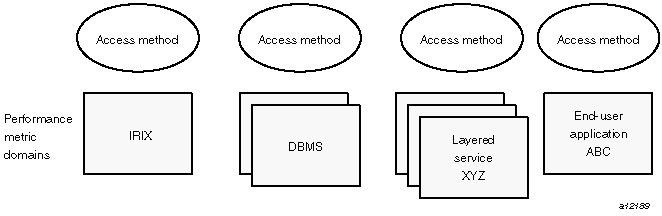
Instrumentation for the purpose of performance monitoring typically consists of counts of activity or events, attribution of resource consumption, and service-time or response-time measures. This instrumentation may exist in one or more of the functional domains as shown in Figure 1-1.
Each domain has an associated access method:
The IRIX kernel, including sar data structures, per-process resource consumption, network statistics, disk activity, or memory management instrumentation.
A layered software service such as activity logs for a World Wide Web server or an NNTP news server.
An application program such as measured response time for a production application running a periodic and benign probe transaction (as often required in service quality agreements), or rate of computation and throughput in jobs per hour for a batch stream.
A layered system product such as the temperature, voltage levels, and fan speeds from the environmental monitor in a Challenge system, or the length of the mail queue as reported by mqueue.
For each domain, the set of performance metrics may be viewed as an abstract data type, with an associated set of methods that may be used to perform the following tasks:
Interrogate the metadata that describes the syntax and semantics of the performance metrics
Control (enable or disable) the collection of some or all of the metrics
Extract instantiations (current values) for some or all of the metrics
We refer to each functional domain as a performance metrics domain and assume that domains are functionally, architecturally, and administratively independent and autonomous. Obviously the set of performance metrics domains available on any host is variable, and changes with time as software and hardware are installed and removed.
The number of performance metrics domains may be further enlarged in cluster-based or network-based configurations, where there is potentially an instance of each performance metrics domain on each node. Hence, the management of performance metrics domains must be both extensible at a particular host and distributed across a number of hosts.
Each performance metrics domain on a particular host must be assigned a unique Performance Metric Identifier (PMID). In practice, this means unique identifiers are assigned globally for each performance metrics domain type. For example, the same identifier would be used for the IRIX performance metrics domain on all hosts.
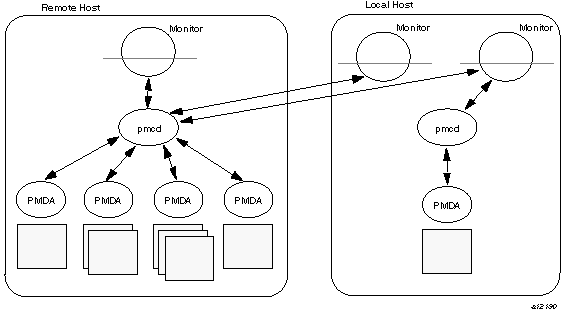
The performance metrics collection architecture is distributed, in the sense that any performance tool may be executing remotely. However, a PMDA must run on the system for which it is collecting performance measurements. In most cases, connecting these tools together on the collector host is the responsibility of the PMCD process, as shown in Figure 1-2.
The host running the monitoring tools does not require any collection tools, including pmcd, because all requests for metrics are sent to the pmcd process on the collector host. These requests are then forwarded to the appropriate PMDAs, which respond with metric descriptions, help text, and most importantly, metric values.
The connections between monitor clients and pmcd processes are managed in libpcp, below the PMAPI level; see the pmapi(3) man page. Connections between PMDAs and pmcd are managed by the PMDA routines; see the pmda(3) man page. There can be multiple monitor clients and multiple PMDAs on the one host, but there may be at most one pmcd process.
Internally, each unique performance metric is identified by a Performance Metric Identifier (PMID) drawn from a universal set of identifiers, including some that are reserved for site-specific, application-specific, and customer-specific use.
An external name space called Performance Metrics Name Space (PMNS) maps from a hierarchy (or tree) of external names to PMIDs.
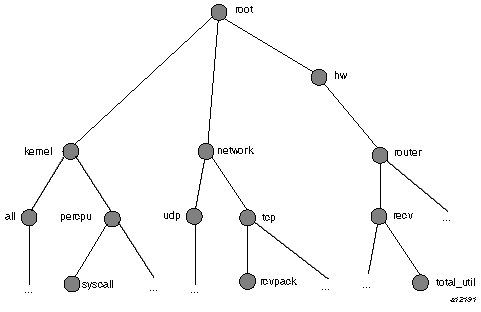
Each node in the PMNS tree is assigned a label that must begin with an alphabet character, and be followed by zero or more alphanumeric characters or the underscore (_) character. The root node of the tree has the special label of root.
A metric name is formed by traversing the tree from the root to a leaf node with each node label on the path separated by a period. The common prefix root. is omitted from all names. For example, Figure 1-3 shows the nodes in a small subsection of a PMNS.
In this subsection, the following are valid names for performance metrics:
kernel.percpu.syscall network.tcp.rcvpack hw.router.recv.total_util |
Although a default PMNS is shipped and updated by the components of PCP, individual users may create their own Name Space for metrics of interest, and all tools may use a private PMNS, rather than the default PMNS.
Through the various performance metric domains, the PCP must support a wide range of formats and semantics for performance metrics. This metadata describing the performance metrics includes the following:
The internal identifier, Performance Metric Identifier (PMID), for the metric
The format and encoding for the values of the metric, for example, an unsigned 32-bit integer or a string or a 64-bit IEEE format floating point number
The semantics of the metric, particularly the interpretation of the values as free-running counters or instantaneous values
The dimensionality of the values, in the dimensions of events, space, and time
The scale of values; for example, bytes, kilobytes (KB), or megabytes (MB) for the space dimension
An indication if the metric may have one or many associated values
Short (and extended) help text describing the metric
For each metric, this metadata is defined within the associated PMDA, and PCP arranges for the information to be exported to the performance tools applications that use the metadata when interpreting the values for performance metrics.
The following sections describe two types of performance metrics, single-valued and set-valued.
Some performance metrics have a singular value within their performance metric domains. For example, available memory (or the total number of context switches) has only one value per performance metric domain, that is, one value per host. The metadata describing the metric makes this fact known to applications that process values for these metrics.
Some performance metrics have a set of values or instances in each implementing performance metric domain. For example, one value for each disk, one value for each process, one value for each CPU, or one value for each activation of a given application.
When a metric has multiple instances, the PCP framework does not pollute the Name Space with additional metric names; rather, a single metric may have an associated set of values. These multiple values are associated with the members of an instance domain, such that each instance has a unique instance identifier within the associated instance domain. For example, the “per CPU” instance domain may use the instance identifiers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on to identify the configured processors in the system.
Internally, instance identifiers are encoded as binary values, but each performance metric domain also supports corresponding strings as external names for the instance identifiers, and these names are used at the user interface to the PCP utilities.
For example, the performance metric disk.dev.total counts I/O operations for each disk spindle, and the associated instance domain contains one member for each disk spindle. On a system with five specific disks, one value would be associated with each of the external and internal instance identifier pairs shown in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1. Sample Instance Identifiers for Disk Statistics
External Instance Identifier | Internal Instance Identifier |
|---|---|
dks1d1 | 131329 |
dks1d2 | 131330 |
dks1d3 | 131331 |
dks3d1 | 131841 |
dks3d2 | 131842 |
Multiple performance metrics may be associated with a single instance domain.
Each performance metric domain may dynamically establish the instances within an instance domain. For example, there may be one instance for the metric kernel.percpu.idle on a workstation, but multiple instances on a multiprocessor server. Even more dynamic is filesys.free, where the values report the amount of free space per file system, and the number of values tracks the mounting and unmounting of local filesystems.
PCP arranges for information describing instance domains to be exported from the performance metric domains to the applications that require this information. Applications may also choose to retrieve values for all instances of a performance metric, or some arbitrary subset of the available instances.
Hosts supporting PCP services are broadly classified into two categories:
Each PCP enabled host can operate as a collector, a monitor, or both.
PCP provides an infrastructure through the Performance Metrics Collection Subsystem (PMCS). It unifies the autonomous and distributed PMDAs into a cohesive pool of performance data, and provides the services required to create generalized and powerful performance tools.
The PMCS provides the framework that underpins the PMAPI. The PMCS is responsible for the following services on behalf of the performance tools developed on top of the PMAPI:
Coordination with the processes and procedures required to control the description, collection, and extraction of performance metric values from agents that interface to the performance metric domains
Servicing incoming requests for local performance metric values and metadata from applications running either locally or on a remote system
The PMCS described in the previous section is used when PMAPI clients are requesting performance metrics from a real-time or live source.
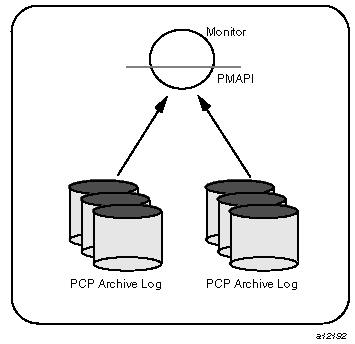
The PMAPI also supports delivery of performance metrics from a historical source in the form of a PCP archive log. Archive logs are created using the pmlogger utility, and are replayed in an architecture as shown in Figure 1-4.
The PMAPI has been designed to minimize the differences required for an application to process performance data from an archive or from a real-time source. As a result, most PCP tools support live and retrospective monitoring with equal facility.
Much of the PCP product's potential for attacking difficult performance problems in production environments comes from the design philosophy that considers extensibility to be critically important.
The performance analyst can take advantage of the PCP infrastructure to deploy value-added performance monitoring tools and services. Here are some examples:
Easy extension of the PMCS and PMNS to accommodate new performance metrics and new sources of performance metrics, in particular using the interfaces of a special-purpose library to develop new PMDAs (see the pmda(3) man page)
Use of libraries (libpcp_pmda and libpcp_trace) to aid in the development of new PMDAs to export performance metrics from local applications
Operation on any performance metric using generalized toolkits
Distribution of PCP components such as collectors across the network, placing the service where it can do the most good
Dynamic adjustment to changes in system configuration
Flexible customization built into the design of all PCP tools
Creation of new monitor applications, using the routines described in the pmapi(3) man page